Page 131 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 131
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM SECTION II 87
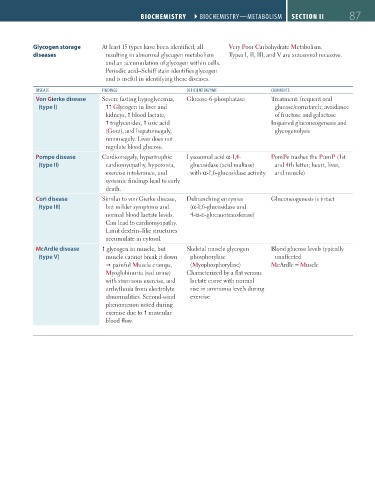
Glycogen storage At least 15 types have been identified, all Very Poor Carbohydrate Metabolism.
diseases resulting in abnormal glycogen metabolism Types I, II, III, and V are autosomal recessive.
and an accumulation of glycogen within cells.
Periodic acid–Schiff stain identifies glycogen
and is useful in identifying these diseases.
DISEASE FINDINGS DEFICIENT ENZYME COMMENTS
Von Gierke disease Severe fasting hypoglycemia, Glucose-6-phosphatase Treatment: frequent oral
(type I) Glycogen in liver and glucose/cornstarch; avoidance
kidneys, blood lactate, of fructose and galactose
triglycerides, uric acid Impaired gluconeogenesis and
(Gout), and hepatomegaly, glycogenolysis
renomegaly. Liver does not
regulate blood glucose.
Pompe disease Cardiomegaly, hypertrophic Lysosomal acid α-1,4- PomPe trashes the PumP (1st
(type II) cardiomyopathy, hypotonia, glucosidase (acid maltase) and 4th letter; heart, liver,
exercise intolerance, and with α-1,6-glucosidase activity and muscle)
systemic findings lead to early
death.
Cori disease Similar to von Gierke disease, Debranching enzymes Gluconeogenesis is intact
(type III) but milder symptoms and (α-1,6-glucosidase and
normal blood lactate levels. 4-α-d-glucanotransferase)
Can lead to cardiomyopathy.
Limit dextrin–like structures
accumulate in cytosol.
McArdle disease glycogen in muscle, but Skeletal muscle glycogen Blood glucose levels typically
(type V) muscle cannot break it down phosphorylase unaffected
painful Muscle cramps, (Myophosphorylase) McArdle = Muscle
Myoglobinuria (red urine) Characterized by a flat venous
with strenuous exercise, and lactate curve with normal
arrhythmia from electrolyte rise in ammonia levels during
abnormalities. Second-wind exercise
phenomenon noted during
exercise due to muscular
blood flow.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 87 11/7/19 3:16 PM