Page 130 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 130
86 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM
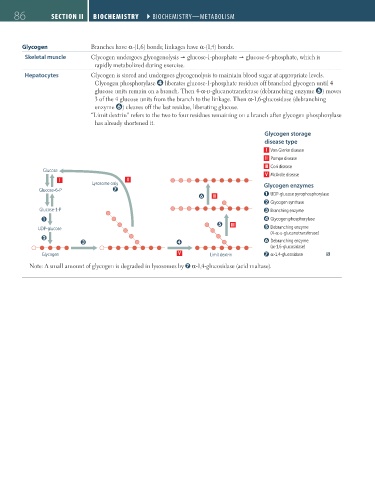
Glycogen Branches have α-(1,6) bonds; linkages have α-(1,4) bonds.
Skeletal muscle Glycogen undergoes glycogenolysis glucose-1-phosphate glucose-6-phosphate, which is
rapidly metabolized during exercise.
Hepatocytes Glycogen is stored and undergoes glycogenolysis to maintain blood sugar at appropriate levels.
Glycogen phosphorylase liberates glucose-1-phosphate residues off branched glycogen until 4
glucose units remain on a branch. Then 4-α-d-glucanotransferase (debranching enzyme ) moves
3 of the 4 glucose units from the branch to the linkage. Then α-1,6-glucosidase (debranching
enzyme ) cleaves off the last residue, liberating glucose.
“Limit dextrin” refers to the two to four residues remaining on a branch after glycogen phosphorylase
has already shortened it.
Glycogen storage
disease type
I Von Gierke disease
II Pompe disease
III Cori disease
Glucose
V McArdle disease
I II
Lysosome only Glycogen enzymes
Glucose-6-P
III UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
Glycogen synthase
Glucose-1-P Branching enzyme
Glycogen phosphorylase
III
UDP-glucose Debranching enzyme
(4-α-D-glucanotransferase)
Debranching enzyme
(α-1,6-glucosidase)
Glycogen V Limit dextrin α-1,4-glucosidase
Note: A small amount of glycogen is degraded in lysosomes by α-1,4-glucosidase (acid maltase).
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 86 11/7/19 3:16 PM