Page 133 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 133
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM SECTION II 89
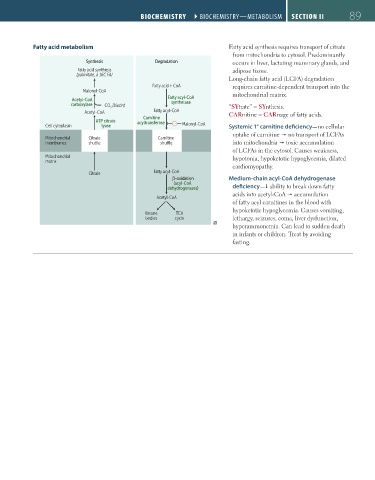
Fatty acid metabolism Fatty acid synthesis requires transport of citrate
from mitochondria to cytosol. Predominantly
Synthesis Degradation occurs in liver, lactating mammary glands, and
Fatty acid synthesis adipose tissue.
(palmitate, a 16C FA)
Long-chain fatty acid (LCFA) degradation
Fatty acid + CoA requires carnitine-dependent transport into the
Malonyl-CoA mitochondrial matrix.
Fatty acyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
carboxylase CO (biotin) synthetase “SYtrate” = SYnthesis.
2
Acetyl-CoA Fatty acyl-CoA CARnitine = CARnage of fatty acids.
Carnitine
ATP citrate acyltransferase −
Cell cytoplasm lyase Malonyl-CoA Systemic 1° carnitine deficiency—no cellular
uptake of carnitine no transport of LCFAs
Mitochondrial Citrate Carnitine
membranes shuttle shuttle into mitochondria toxic accumulation
of LCFAs in the cytosol. Causes weakness,
Mitochondrial hypotonia, hypoketotic hypoglycemia, dilated
matrix
cardiomyopathy.
Citrate Fatty acyl-CoA
β-oxidation Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
(acyl-CoA
dehydrogenases) deficiency— ability to break down fatty
acids into acetyl-CoA accumulation
Acetyl-CoA
of fatty acyl carnitines in the blood with
hypoketotic hypoglycemia. Causes vomiting,
Ketone TCA
bodies cycle lethargy, seizures, coma, liver dysfunction,
hyperammonemia. Can lead to sudden death
in infants or children. Treat by avoiding
fasting.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 89 11/7/19 3:16 PM