Page 135 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 135
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—METABOlISM SECTION II 91
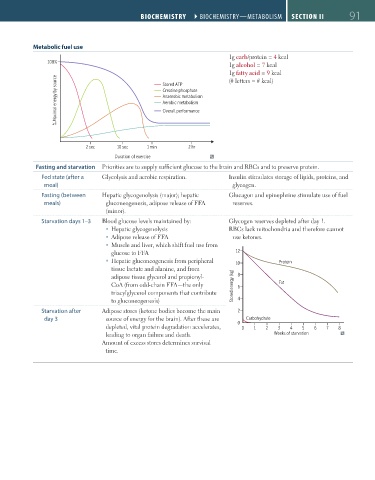
Metabolic fuel use
1g carb/protein = 4 kcal
100% 1g alcohol = 7 kcal
12 1g fatty acid = 9 kcal
10 Protein Stored ATP (# letters = # kcal)
Creatine phosphate
Stored energy (kg) 8 6 Fat % Maximal energy by source Anaerobic metabolism
Aerobic metabolism
Overall performance
2 4
Carbohydrate
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 sec 10 sec 1 min 2 hr
Weeks of starvation
Duration of exercise
Fasting and starvation Priorities are to supply sufficient glucose to the brain and RBCs and to preserve protein.
Fed state (after a Glycolysis and aerobic respiration. Insulin stimulates storage of lipids, proteins, and
meal) glycogen.
Fasting (between Hepatic glycogenolysis (major); hepatic Glucagon and epinephrine stimulate use of fuel
meals) gluconeogenesis, adipose release of FFA reserves.
(minor).
Starvation days 1–3 Blood glucose levels maintained by: Glycogen reserves depleted after day 1.
Hepatic glycogenolysis RBCs lack mitochondria and therefore cannot
Adipose release of FFA use ketones.
Muscle and liver, which shift fuel use from 100%
glucose to FFA 12
Hepatic gluconeogenesis from peripheral 10 Protein
tissue lactate and alanine, and from Stored ATP
Creatine phosphate
adipose tissue glycerol and propionyl- 8 Anaerobic metabolism
CoA (from odd-chain FFA—the only Stored energy (kg) 6 Fat % Maximal energy by source Aerobic metabolism
triacylglycerol components that contribute Overall performance
to gluconeogenesis) 4
Starvation after Adipose stores (ketone bodies become the main 2
day 3 source of energy for the brain). After these are Carbohydrate
depleted, vital protein degradation accelerates, 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 sec 10 sec 1 min 2 hrs
leading to organ failure and death. Weeks of starvation Time
Amount of excess stores determines survival
time.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 91 11/7/19 3:16 PM