Page 148 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 148
104 SECTIon II Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS
` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS
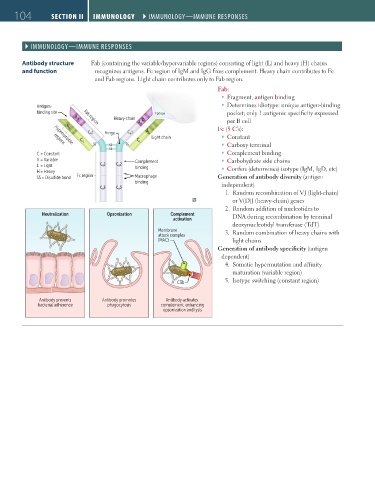
Antibody structure Fab (containing the variable/hypervariable regions) consisting of light (L) and heavy (H) chains
and function recognizes antigens. Fc region of IgM and IgG fixes complement. Heavy chain contributes to Fc
and Fab regions. Light chain contributes only to Fab region.
Fab:
Fragment, antigen binding
Antigen- Determines idiotype: unique antigen-binding
binding site Epitope pocket; only 1 antigenic specificity expressed
V H Fab region Heavy chain D
J H per B cell
V L Fc (5 C’s):
C H 1 Hinge C H 1 J L
C L C L Light chain Constant
Hypervariable
regions
SS SS SS Carboxy terminal
SS
C = Constant Complement binding
V = Variable Complement Carbohydrate side chains
L = Light C H 2 C H 2 binding Confers (determines) isotype (IgM, IgD, etc)
H = Heavy
SS = Disulfide bond Fc region Macrophage Generation of antibody diversity (antigen
binding independent)
C H 3 C H 3
1. Random recombination of VJ (light-chain)
or V(D)J (heavy-chain) genes
2. Random addition of nucleotides to
Neutralization Opsonization Complement DNA during recombination by terminal
activation
deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)
Membrane 3. Random combination of heavy chains with
attack complex
(MAC) light chains
Generation of antibody specificity (antigen
dependent)
4. Somatic hypermutation and affinity
maturation (variable region)
5. Isotype switching (constant region)
C3b
Antibody prevents Antibody promotes Antibody activates
bacterial adherence phagocytosis complement, enhancing
opsonization and lysis
FAS1_2019_02-Immunology.indd 104 11/7/19 3:24 PM