Page 146 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 146
102 SECTIon II Immunology ` Immunology—cellular componentS Immunology ` Immunology—cellular componentS
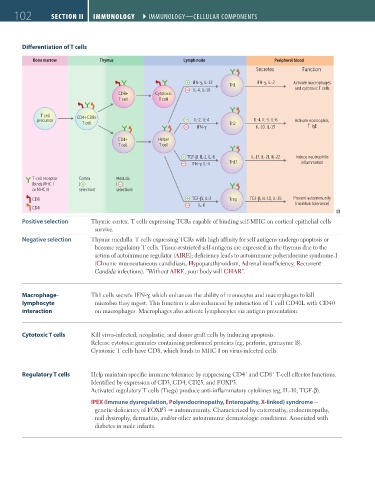
Differentiation of T cells
Bone marrow Thymus Lymph node Peripheral blood
Secretes Function
IFN-γ, IL-12 IFN-γ, IL-2 Activate macrophages
Th1
IL-4, IL-10 and cytotoxic T cells
CD8+ Cytotoxic
T cell T cell
T cell CD4+CD8+
precursor IL-2, IL-4 IL-4, IL-5, IL-6 Activate eosinophils,
T cell Th2
IFN-γ IL-10, IL-13 ↑ IgE
CD4+ Helper
T cell T cell
TGF-β, IL-1, IL-6 IL-17, IL-21, IL-22 Induce neutrophilic
IFN-γ, IL-4 Th17 inflammation
T-cell receptor Cortex Medulla
(binds MHC I ( (
or MHC II) selection) selection)
CD8 TGF-β, IL-2 Treg TGF-β, IL-10, IL-35 Prevent autoimmunity
IL-6 (maintain tolerance)
CD4
Positive selection Thymic cortex. T cells expressing TCRs capable of binding self-MHC on cortical epithelial cells
survive.
Negative selection Thymic medulla. T cells expressing TCRs with high affinity for self antigens undergo apoptosis or
become regulatory T cells. Tissue-restricted self-antigens are expressed in the thymus due to the
action of autoimmune regulator (AIRE); deficiency leads to autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome-1
(Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, Hypoparathyroidism, Adrenal insufficiency, Recurrent
Candida infections). “Without AIRE, your body will CHAR”.
Macrophage- Th1 cells secrete IFN-γ, which enhances the ability of monocytes and macrophages to kill
lymphocyte microbes they ingest. This function is also enhanced by interaction of T cell CD40L with CD40
interaction on macrophages. Macrophages also activate lymphocytes via antigen presentation.
Cytotoxic T cells Kill virus-infected, neoplastic, and donor graft cells by inducing apoptosis.
Release cytotoxic granules containing preformed proteins (eg, perforin, granzyme B).
Cytotoxic T cells have CD8, which binds to MHC I on virus-infected cells.
Regulatory T cells Help maintain specific immune tolerance by suppressing CD4 and CD8 T-cell effector functions.
+
+
Identified by expression of CD3, CD4, CD25, and FOXP3.
Activated regulatory T cells (Tregs) produce anti-inflammatory cytokines (eg, IL-10, TGF-β).
IPEX (Immune dysregulation, Polyendocrinopathy, Enteropathy, X-linked) syndrome—
genetic deficiency of FOXP3 autoimmunity. Characterized by enteropathy, endocrinopathy,
nail dystrophy, dermatitis, and/or other autoimmune dermatologic conditions. Associated with
diabetes in male infants.
FAS1_2019_02-Immunology.indd 102 11/7/19 3:24 PM