Page 143 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 143
Immunology ` Immunology—lymphoId StructureS Immunology ` Immunology—cellular componentS SECTIon II 99
` Immunology—cellular componentS
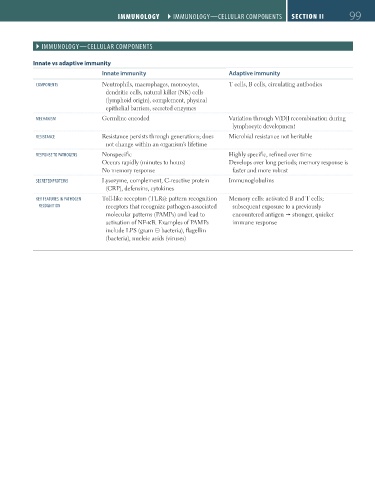
Innate vs adaptive immunity
Innate immunity Adaptive immunity
componentS Neutrophils, macrophages, monocytes, T cells, B cells, circulating antibodies
dendritic cells, natural killer (NK) cells
(lymphoid origin), complement, physical
epithelial barriers, secreted enzymes
mechanISm Germline encoded Variation through V(D)J recombination during
lymphocyte development
reSIStance Resistance persists through generations; does Microbial resistance not heritable
not change within an organism’s lifetime
reSponSe to pathogenS Nonspecific Highly specific, refined over time
Occurs rapidly (minutes to hours) Develops over long periods; memory response is
No memory response faster and more robust
Secreted proteInS Lysozyme, complement, C-reactive protein Immunoglobulins
(CRP), defensins, cytokines
Key FeatureS In pathogen Toll-like receptors (TLRs): pattern recognition Memory cells: activated B and T cells;
recognItIon receptors that recognize pathogen-associated subsequent exposure to a previously
molecular patterns (PAMPs) and lead to encountered antigen stronger, quicker
activation of NF-κB. Examples of PAMPs immune response
include LPS (gram ⊝ bacteria), flagellin
(bacteria), nucleic acids (viruses)
FAS1_2019_02-Immunology.indd 99 11/7/19 3:24 PM