Page 163 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 163
Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS SECTIon II 119
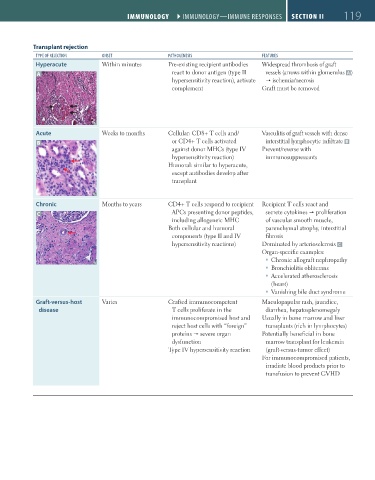
Transplant rejection
type oF reJectIon onSet pathogeneSIS FeatureS
Hyperacute Within minutes Pre-existing recipient antibodies Widespread thrombosis of graft
A react to donor antigen (type II vessels (arrows within glomerulus A)
hypersensitivity reaction), activate ischemia/necrosis
complement Graft must be removed
Acute Weeks to months Cellular: CD8+ T cells and/ Vasculitis of graft vessels with dense
B or CD4+ T cells activated interstitial lymphocytic infiltrate B
against donor MHCs (type IV Prevent/reverse with
hypersensitivity reaction) immunosuppressants
Humoral: similar to hyperacute,
except antibodies develop after
transplant
Chronic Months to years CD4+ T cells respond to recipient Recipient T cells react and
C APCs presenting donor peptides, secrete cytokines proliferation
including allogeneic MHC of vascular smooth muscle,
Both cellular and humoral parenchymal atrophy, interstitial
components (type II and IV fibrosis
hypersensitivity reactions) Dominated by arteriosclerosis C
Organ-specific examples:
Chronic allograft nephropathy
Bronchiolitis obliterans
Accelerated atherosclerosis
(heart)
Vanishing bile duct syndrome
Graft-versus-host Varies Grafted immunocompetent Maculopapular rash, jaundice,
disease T cells proliferate in the diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly
immunocompromised host and Usually in bone marrow and liver
reject host cells with “foreign” transplants (rich in lymphocytes)
proteins severe organ Potentially beneficial in bone
dysfunction marrow transplant for leukemia
Type IV hypersensitivity reaction (graft-versus-tumor effect)
For immunocompromised patients,
irradiate blood products prior to
transfusion to prevent GVHD
FAS1_2019_02-Immunology.indd 119 11/7/19 3:24 PM