Page 161 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 161
Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS SECTIon II 117
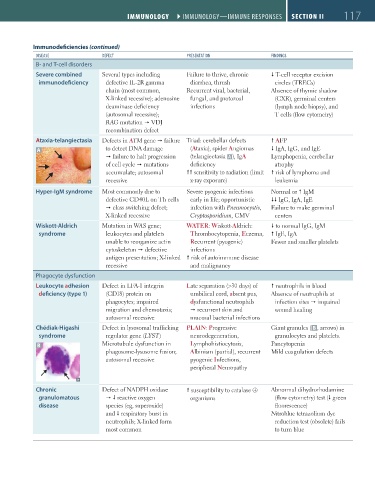
Immunodeficiencies (continued)
dISeaSe deFect preSentatIon FIndIngS
B- and T-cell disorders
Severe combined Several types including Failure to thrive, chronic T-cell receptor excision
immunodeficiency defective IL-2R gamma diarrhea, thrush circles (TRECs)
chain (most common, Recurrent viral, bacterial, Absence of thymic shadow
X-linked recessive); adenosine fungal, and protozoal (CXR), germinal centers
deaminase deficiency infections (lymph node biopsy), and
(autosomal recessive); T cells (flow cytometry)
RAG mutation VDJ
recombination defect
Ataxia-telangiectasia Defects in ATM gene failure Triad: cerebellar defects AFP
A to detect DNA damage (Ataxia), spider Angiomas IgA, IgG, and IgE
failure to halt progression (telangiectasia A), IgA Lymphopenia, cerebellar
of cell cycle mutations deficiency atrophy
accumulate; autosomal sensitivity to radiation (limit risk of lymphoma and
recessive x-ray exposure) leukemia
Hyper-IgM syndrome Most commonly due to Severe pyogenic infections Normal or IgM
defective CD40L on Th cells early in life; opportunistic IgG, IgA, IgE
class switching defect; infection with Pneumocystis, Failure to make germinal
X-linked recessive Cryptosporidium, CMV centers
Wiskott-Aldrich Mutation in WAS gene; WATER: Wiskott-Aldrich: to normal IgG, IgM
syndrome leukocytes and platelets Thrombocytopenia, Eczema, IgE, IgA
unable to reorganize actin Recurrent (pyogenic) Fewer and smaller platelets
cytoskeleton defective infections
antigen presentation; X-linked risk of autoimmune disease
recessive and malignancy
Phagocyte dysfunction
Leukocyte adhesion Defect in LFA-1 integrin Late separation (>30 days) of neutrophils in blood
deficiency (type 1) (CD18) protein on umbilical cord, absent pus, Absence of neutrophils at
phagocytes; impaired dysfunctional neutrophils infection sites impaired
migration and chemotaxis; recurrent skin and wound healing
autosomal recessive mucosal bacterial infections
Chédiak-Higashi Defect in lysosomal trafficking PLAIN: Progressive Giant granules ( B , arrows) in
syndrome regulator gene (LYST) neurodegeneration, granulocytes and platelets.
B Microtubule dysfunction in Lymphohistiocytosis, Pancytopenia
phagosome-lysosome fusion; Albinism (partial), recurrent Mild coagulation defects
autosomal recessive pyogenic Infections,
peripheral Neuropathy
Chronic Defect of NADPH oxidase susceptibility to catalase ⊕ Abnormal dihydrorhodamine
granulomatous reactive oxygen organisms (flow cytometry) test ( green
disease species (eg, superoxide) fluorescence)
and respiratory burst in Nitroblue tetrazolium dye
neutrophils; X-linked form reduction test (obsolete) fails
most common to turn blue
FAS1_2019_02-Immunology.indd 117 11/7/19 3:24 PM