Page 160 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 160
116 SECTIon II Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS
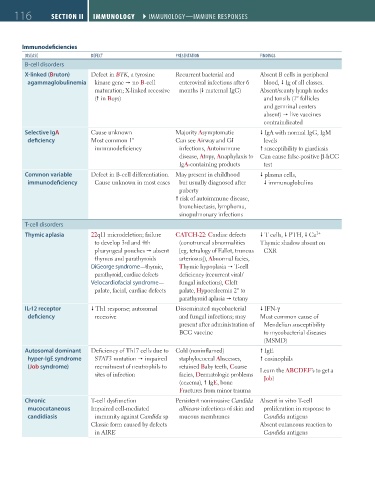
Immunodeficiencies
dISeaSe deFect preSentatIon FIndIngS
B-cell disorders
X-linked (Bruton) Defect in BTK, a tyrosine Recurrent bacterial and Absent B cells in peripheral
agammaglobulinemia kinase gene no B-cell enteroviral infections after 6 blood, Ig of all classes.
maturation; X-linked recessive months ( maternal IgG) Absent/scanty lymph nodes
( in Boys) and tonsils (1° follicles
and germinal centers
absent) live vaccines
contraindicated
Selective IgA Cause unknown Majority Asymptomatic IgA with normal IgG, IgM
deficiency Most common 1° Can see Airway and GI levels
immunodeficiency infections, Autoimmune susceptibility to giardiasis
disease, Atopy, Anaphylaxis to Can cause false-positive β-hCG
IgA-containing products test
Common variable Defect in B-cell differentiation. May present in childhood plasma cells,
immunodeficiency Cause unknown in most cases but usually diagnosed after immunoglobulins
puberty
risk of autoimmune disease,
bronchiectasis, lymphoma,
sinopulmonary infections
T-cell disorders
Thymic aplasia 22q11 microdeletion; failure CATCH-22: Cardiac defects T cells, PTH, Ca 2+
to develop 3rd and 4th (conotruncal abnormalities Thymic shadow absent on
pharyngeal pouches absent [eg, tetralogy of Fallot, truncus CXR
thymus and parathyroids arteriosus]), Abnormal facies,
DiGeorge syndrome—thymic, Thymic hypoplasia T-cell
parathyroid, cardiac defects deficiency (recurrent viral/
Velocardiofacial syndrome— fungal infections), Cleft
palate, facial, cardiac defects palate, Hypocalcemia 2° to
parathyroid aplasia tetany
IL-12 receptor Th1 response; autosomal Disseminated mycobacterial IFN-γ
deficiency recessive and fungal infections; may Most common cause of
present after administration of Mendelian susceptibility
BCG vaccine to mycobacterial diseases
(MSMD)
Autosomal dominant Deficiency of Th17 cells due to Cold (noninflamed) IgE
hyper-IgE syndrome STAT3 mutation impaired staphylococcal Abscesses, eosinophils
(Job syndrome) recruitment of neutrophils to retained Baby teeth, Coarse Learn the ABCDEF’s to get a
sites of infection facies, Dermatologic problems Job!
(eczema), IgE, bone
Fractures from minor trauma
Chronic T-cell dysfunction Persistent noninvasive Candida Absent in vitro T-cell
mucocutaneous Impaired cell-mediated albicans infections of skin and proliferation in response to
candidiasis immunity against Candida sp mucous membranes Candida antigens
Classic form caused by defects Absent cutaneous reaction to
in AIRE Candida antigens
FAS1_2019_02-Immunology.indd 116 11/7/19 3:24 PM