Page 158 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 158
114 SECTIon II Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS Immunology ` Immunology—Immune reSponSeS
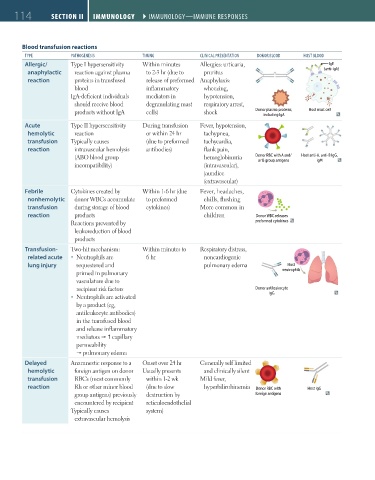
Blood transfusion reactions
type pathogeneSIS tImIng clInIcal preSentatIon donor Blood hoSt Blood
Allergic/ Type I hypersensitivity Within minutes Allergies: urticaria, IgE
anaphylactic reaction against plasma to 2-3 hr (due to pruritus (anti-IgA)
reaction proteins in transfused release of preformed Anaphylaxis:
blood inflammatory wheezing,
IgA-deficient individuals mediators in hypotension,
should receive blood degranulating mast respiratory arrest,
products without IgA cells) shock Donor plasma proteins, Host mast cell
including IgA
Acute Type II hypersensitivity During transfusion Fever, hypotension,
hemolytic reaction or within 24 hr tachypnea,
transfusion Typically causes (due to preformed tachycardia,
reaction intravascular hemolysis antibodies) flank pain,
(ABO blood group hemoglobinuria Donor RBC with A and/ Host anti-A, anti-B IgG,
IgM
or B group antigens
incompatibility) (intravascular),
jaundice
(extravascular)
Febrile Cytokines created by Within 1-6 hr (due Fever, headaches,
nonhemolytic donor WBCs accumulate to preformed chills, flushing
transfusion during storage of blood cytokines) More common in
reaction products children Donor WBC releases Host anti-HLA, anti-
Reactions prevented by preformed cytokines leukocyte IgG
leukoreduction of blood
products
Transfusion- Two-hit mechanism: Within minutes to Respiratory distress,
related acute Neutrophils are 6 hr noncardiogenic
lung injury sequestered and pulmonary edema Host
primed in pulmonary neutrophils
vasculature due to
recipient risk factors Donor antileukocyte
Neutrophils are activated IgG
by a product (eg,
antileukocyte antibodies)
in the transfused blood
and release inflammatory
mediators capillary
permeability
pulmonary edema
Delayed Anamnestic response to a Onset over 24 hr Generally self limited
hemolytic foreign antigen on donor Usually presents and clinically silent
transfusion RBCs (most commonly within 1-2 wk Mild fever,
reaction Rh or other minor blood (due to slow hyperbilirubinemia Donor RBC with Host IgG
group antigens) previously destruction by foreign antigens
encountered by recipient reticuloendothelial
Typically causes system)
extravascular hemolysis
FAS1_2019_02-Immunology.indd 114 11/7/19 3:24 PM