Page 195 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 195
Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology Microbiology ` microbiology—mycology SEcTioN ii 151
` microbiology—mycology
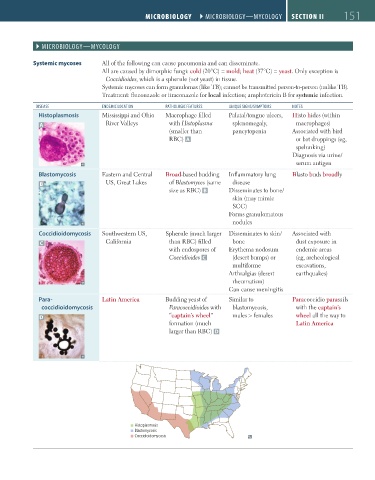
Systemic mycoses All of the following can cause pneumonia and can disseminate.
All are caused by dimorphic fungi: cold (20°C) = mold; heat (37°C) = yeast. Only exception is
Coccidioides, which is a spherule (not yeast) in tissue.
Systemic mycoses can form granulomas (like TB); cannot be transmitted person-to-person (unlike TB).
Treatment: fluconazole or itraconazole for local infection; amphotericin B for systemic infection.
Disease eNDemic locatioN PatHologic FeatUres UNiQUe sigNs/symPtoms Notes
Histoplasmosis Mississippi and Ohio Macrophage filled Palatal/tongue ulcers, Histo hides (within
A River Valleys with Histoplasma splenomegaly, macrophages)
(smaller than pancytopenia Associated with bird
RBC) A or bat droppings (eg,
spelunking)
Diagnosis via urine/
serum antigen
Blastomycosis Eastern and Central Broad-based budding Inflammatory lung Blasto buds broadly
B US, Great Lakes of Blastomyces (same disease
size as RBC) B Disseminates to bone/
skin (may mimic
SCC)
Forms granulomatous
nodules
Coccidioidomycosis Southwestern US, Spherule (much larger Disseminates to skin/ Associated with
C California than RBC) filled bone dust exposure in
with endospores of Erythema nodosum endemic areas
Coccidioides C (desert bumps) or (eg, archeological
multiforme excavations,
Arthralgias (desert earthquakes)
rheumatism)
Can cause meningitis
Para- Latin America Budding yeast of Similar to Paracoccidio parasails
coccidioidomycosis Paracoccidioides with blastomycosis, with the captain’s
D “captain’s wheel” males > females wheel all the way to
formation (much Latin America
larger than RBC) D
Histoplasmosis
Blastomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 151 11/14/19 12:21 PM