Page 191 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 191
Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology SEcTioN ii 147
Leptospira interrogans Spirochete with hook-shaped ends found in water contaminated with animal urine.
Leptospirosis—flu-like symptoms, myalgias (classically of calves), jaundice, photophobia with
conjunctival suffusion (erythema without exudate). Prevalent among surfers and in tropics (eg,
Hawaii).
Weil disease (icterohemorrhagic leptospirosis)—severe form with jaundice and azotemia from liver
and kidney dysfunction, fever, hemorrhage, and anemia.
Syphilis Caused by spirochete Treponema pallidum. Treatment: penicillin G.
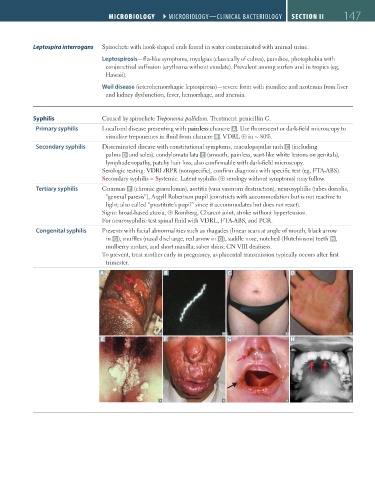
Primary syphilis Localized disease presenting with painless chancre A . Use fluorescent or dark-field microscopy to
visualize treponemes in fluid from chancre B . VDRL ⊕ in ~ 80%.
Secondary syphilis Disseminated disease with constitutional symptoms, maculopapular rash C (including
palms D and soles), condylomata lata E (smooth, painless, wart-like white lesions on genitals),
lymphadenopathy, patchy hair loss; also confirmable with dark-field microscopy.
Serologic testing: VDRL/RPR (nonspecific), confirm diagnosis with specific test (eg, FTA-ABS).
Secondary syphilis = Systemic. Latent syphilis (⊕ serology without symptoms) may follow.
Tertiary syphilis Gummas F (chronic granulomas), aortitis (vasa vasorum destruction), neurosyphilis (tabes dorsalis,
“general paresis”), Argyll Robertson pupil (constricts with accommodation but is not reactive to
light; also called “prostitute’s pupil” since it accommodates but does not react).
Signs: broad-based ataxia, ⊕ Romberg, Charcot joint, stroke without hypertension.
For neurosyphilis: test spinal fluid with VDRL, FTA-ABS, and PCR.
Congenital syphilis Presents with facial abnormalities such as rhagades (linear scars at angle of mouth, black arrow
in G), snuffles (nasal discharge, red arrow in G), saddle nose, notched (Hutchinson) teeth H,
mulberry molars, and short maxilla; saber shins; CN VIII deafness.
To prevent, treat mother early in pregnancy, as placental transmission typically occurs after first
trimester.
A B C D
E F G H
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 147 11/14/19 12:20 PM