Page 255 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 255
Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—CeLLuLAr InjurY Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—CeLLuLAr InjurY SECtIoN II 211
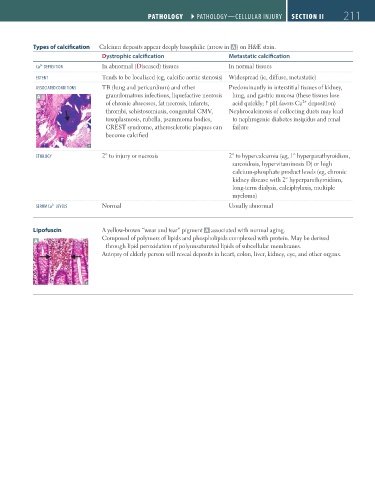
Types of calcification Calcium deposits appear deeply basophilic (arrow in A ) on H&E stain.
Dystrophic calcification Metastatic calcification
2+
Ca DePOSITIOn In abnormal (Diseased) tissues In normal tissues
eXTenT Tends to be localized (eg, calcific aortic stenosis) Widespread (ie, diffuse, metastatic)
ASSOCIATeD COnDITIOnS TB (lung and pericardium) and other Predominantly in interstitial tissues of kidney,
A granulomatous infections, liquefactive necrosis lung, and gastric mucosa (these tissues lose
2+
of chronic abscesses, fat necrosis, infarcts, acid quickly; pH favors Ca deposition)
thrombi, schistosomiasis, congenital CMV, Nephrocalcinosis of collecting ducts may lead
toxoplasmosis, rubella, psammoma bodies, to nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and renal
CREST syndrome, atherosclerotic plaques can failure
become calcified
eTIOLOGY 2° to injury or necrosis 2° to hypercalcemia (eg, 1° hyperparathyroidism,
sarcoidosis, hypervitaminosis D) or high
calcium-phosphate product levels (eg, chronic
kidney disease with 2° hyperparathyroidism,
long-term dialysis, calciphylaxis, multiple
myeloma)
SeruM Ca LeVeLS Normal Usually abnormal
2+
Lipofuscin A yellow-brown “wear and tear” pigment A associated with normal aging.
Composed of polymers of lipids and phospholipids complexed with protein. May be derived
A
through lipid peroxidation of polyunsaturated lipids of subcellular membranes.
Autopsy of elderly person will reveal deposits in heart, colon, liver, kidney, eye, and other organs.
FAS1_2019_04-Pathol.indd 211 11/7/19 4:02 PM