Page 257 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 257
Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—CeLLuLAr InjurY Pathology ` PATHOLOGY—InfLAMMATIOn SECtIoN II 213
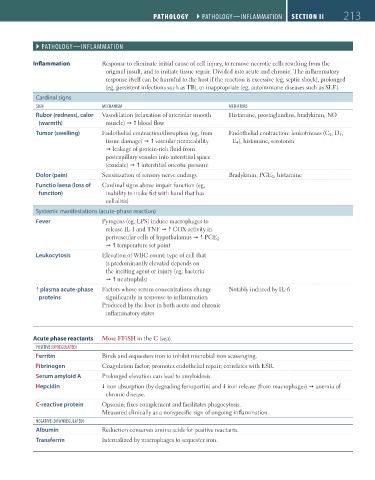
` PATHOLOGY—InfLAMMATIOn
Inflammation Response to eliminate initial cause of cell injury, to remove necrotic cells resulting from the
original insult, and to initiate tissue repair. Divided into acute and chronic. The inflammatory
response itself can be harmful to the host if the reaction is excessive (eg, septic shock), prolonged
(eg, persistent infections such as TB), or inappropriate (eg, autoimmune diseases such as SLE).
Cardinal signs
SIGn MeCHAnISM MeDIATOrS
Rubor (redness), calor Vasodilation (relaxation of arteriolar smooth Histamine, prostaglandins, bradykinin, NO
(warmth) muscle) blood flow
Tumor (swelling) Endothelial contraction/disruption (eg, from Endothelial contraction: leukotrienes (C 4 , D 4 ,
tissue damage) vascular permeability E 4 ), histamine, serotonin
leakage of protein-rich fluid from
postcapillary venules into interstitial space
(exudate) interstitial oncotic pressure
Dolor (pain) Sensitization of sensory nerve endings Bradykinin, PGE 2 , histamine
Functio laesa (loss of Cardinal signs above impair function (eg,
function) inability to make fist with hand that has
cellulitis)
Systemic manifestations (acute-phase reaction)
Fever Pyrogens (eg, LPS) induce macrophages to
release IL-1 and TNF COX activity in
perivascular cells of hypothalamus PGE 2
temperature set point
Leukocytosis Elevation of WBC count; type of cell that
is predominantly elevated depends on
the inciting agent or injury (eg, bacteria
neutrophils)
plasma acute-phase Factors whose serum concentrations change Notably induced by IL-6
proteins significantly in response to inflammation
Produced by the liver in both acute and chronic
inflammatory states
Acute phase reactants More FFiSH in the C (sea).
POSITIVe (uPreGuLATeD)
Ferritin Binds and sequesters iron to inhibit microbial iron scavenging.
Fibrinogen Coagulation factor; promotes endothelial repair; correlates with ESR.
Serum amyloid A Prolonged elevation can lead to amyloidosis.
Hepcidin iron absorption (by degrading ferroportin) and iron release (from macrophages) anemia of
chronic disease.
C-reactive protein Opsonin; fixes complement and facilitates phagocytosis.
Measured clinically as a nonspecific sign of ongoing inflammation.
neGATIVe (DOWnreGuLATeD)
Albumin Reduction conserves amino acids for positive reactants.
Transferrin Internalized by macrophages to sequester iron.
FAS1_2019_04-Pathol.indd 213 11/7/19 4:02 PM