Page 327 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 327
CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—EMbRYOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—ANATOMY SECTION III 283
` `CARdIOvASCulAR—ANATOMY
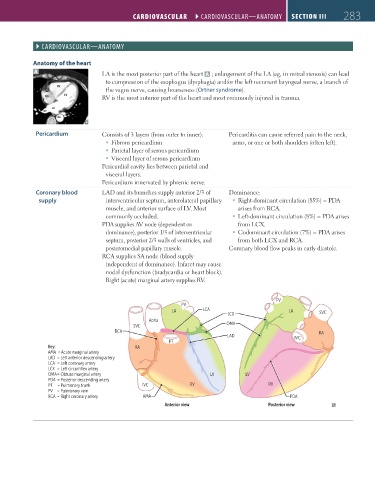
Anatomy of the heart
A LA is the most posterior part of the heart A ; enlargement of the LA (eg, in mitral stenosis) can lead
to compression of the esophagus (dysphagia) and/or the left recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of
RV
the vagus nerve, causing hoarseness (Ortner syndrome).
RA LV RV is the most anterior part of the heart and most commonly injured in trauma.
LA
pv
Ao
Pericardium Consists of 3 layers (from outer to inner): Pericarditis can cause referred pain to the neck,
Fibrous pericardium arms, or one or both shoulders (often left).
Parietal layer of serous pericardium
Visceral layer of serous pericardium
Pericardial cavity lies between parietal and
visceral layers.
Pericardium innervated by phrenic nerve.
Coronary blood LAD and its branches supply anterior 2/3 of Dominance:
supply interventricular septum, anterolateral papillary Right-dominant circulation (85%) = PDA
muscle, and anterior surface of LV. Most arises from RCA.
commonly occluded. Left-dominant circulation (8%) = PDA arises
PDA supplies AV node (dependent on from LCX.
dominance), posterior 1/3 of interventricular Codominant circulation (7%) = PDA arises
septum, posterior 2/3 walls of ventricles, and from both LCX and RCA.
posteromedial papillary muscle. Coronary blood flow peaks in early diastole.
RCA supplies SA node (blood supply
independent of dominance). Infarct may cause
nodal dysfunction (bradycardia or heart block).
Right (acute) marginal artery supplies RV.
PV
PV
LA LCA LA
LCX SVC
Aorta
SVC OMA
RCA RA
LAD IVC
PT
Key: RA
AMA = Acute marginal artery
LAD = Left anterior descending artery
LCA = Left coronary artery
LCX = Left circumflex artery
OMA = Obtuse marginal artery LV LV
PDA = Posterior descending artery
PT = Pulmonary trunk IVC RV RV
PV = Pulmonary vein
RCA = Right coronary artery AMA PDA
Anterior view Posterior view
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 283 11/7/19 4:24 PM