Page 330 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 330
286 SECTION III CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY
Resistance, pressure, ΔP = Q × R Capillaries have highest total cross-sectional
flow Similar to Ohm’s law: ΔV = I × R area and lowest flow velocity.
Volumetric flow rate (Q) = flow velocity (v) × Pressure gradient drives flow from high pressure
cross-sectional area (A) to low pressure.
Resistance Arterioles account for most of TPR. Veins
driving pressure (ΔP) 8η (viscosity) × length provide most of blood storage capacity.
= =
Q πr 4 Viscosity depends mostly on hematocrit.
Total resistance of vessels in series: Viscosity in hyperproteinemic states (eg,
R T = R 1 + R 2 + R 3 . . . multiple myeloma), polycythemia.
Total resistance of vessels in parallel: Viscosity in anemia.
1 1 1 1
=
+
+
R T R 1 R 2 R 3 . . .
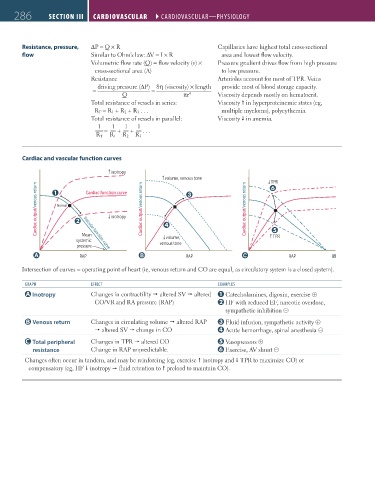
Cardiac and vascular function curves
inotropy
↓
volume, venous tone TPR
↓
↓
Cardiac output/venous return Normal ↓ inotropy Cardiac output/venous return Cardiac output/venous return
Cardiac function curve
Mean
↓
systemic volume, TPR
↓
pressure venous tone
Vascular function curve
A RAP B RAP C RAP
Intersection of curves = operating point of heart (ie, venous return and CO are equal, as circulatory system is a closed system).
GRAPH EFFECT EXAMPlES
Inotropy Changes in contractility altered SV altered Catecholamines, digoxin, exercise ⊕
CO/VR and RA pressure (RAP) HF with reduced EF, narcotic overdose,
sympathetic inhibition ⊝
Venous return Changes in circulating volume altered RAP Fluid infusion, sympathetic activity ⊕
altered SV change in CO Acute hemorrhage, spinal anesthesia ⊝
Total peripheral Changes in TPR altered CO Vasopressors ⊕
resistance Change in RAP unpredictable. Exercise, AV shunt ⊝
Changes often occur in tandem, and may be reinforcing (eg, exercise inotropy and TPR to maximize CO) or
compensatory (eg, HF inotropy fluid retention to preload to maintain CO).
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 286 11/7/19 4:24 PM