Page 329 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 329
CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY SECTION III 285
Cardiac output equations
EQuATION NOTES
Stroke volume SV = EDV − ESV
Ejection fraction EF = SV EDV − ESV EF is an index of ventricular contractility ( in
=
EDV EDV systolic HF; usually normal in diastolic HF).
Cardiac output CO = SV × HR In early stages of exercise, CO maintained by
HR and SV. In later stages, CO maintained
Fick principle: by HR only (SV plateaus).
rate of O 2 consumption Diastole is shortened with HR (eg, ventricular
CO =
(arterial O 2 content – venous O 2 content) tachycardia) diastolic filling time SV
CO.
Pulse pressure PP = SBP – DBP PP directly proportional to SV and inversely
proportional to arterial compliance.
PP in hyperthyroidism, aortic regurgitation,
aortic stiffening (isolated systolic hypertension
in elderly), obstructive sleep apnea
( sympathetic tone), anemia, exercise
(transient).
PP in aortic stenosis, cardiogenic shock,
cardiac tamponade, advanced HF.
Mean arterial pressure MAP = CO × TPR MAP (at resting HR) = 2/3 DBP + 1/3 SBP =
DBP + 1/3 PP.
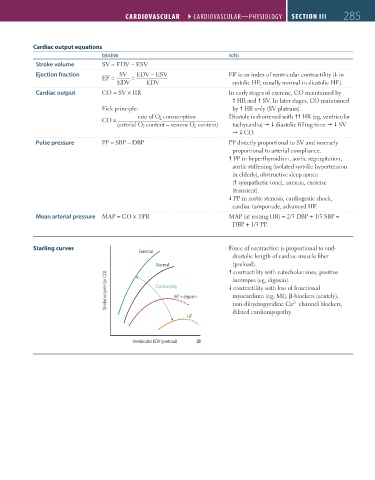
Starling curves Force of contraction is proportional to end-
Exercise
diastolic length of cardiac muscle fiber
(preload).
Normal contractility with catecholamines, positive
Stroke volume (or CO) Contractility HF + digoxin contractility with loss of functional
inotropes (eg, digoxin).
myocardium (eg, MI), β-blockers (acutely),
non-dihydropyridine Ca channel blockers,
2+
HF dilated cardiomyopathy.
Ventricular EDV (preload)
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 285 11/7/19 4:24 PM