Page 328 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 328
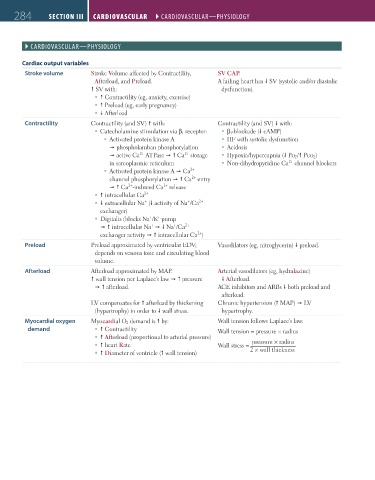
284 SECTION III CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY
` `CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY
Cardiac output variables
Stroke volume Stroke Volume affected by Contractility, SV CAP.
Afterload, and Preload. A failing heart has SV (systolic and/or diastolic
SV with: dysfunction).
Contractility (eg, anxiety, exercise)
Preload (eg, early pregnancy)
Afterload
Contractility Contractility (and SV) with: Contractility (and SV) with:
Catecholamine stimulation via β 1 receptor: β 1 -blockade ( cAMP)
Activated protein kinase A HF with systolic dysfunction
phospholamban phosphorylation Acidosis
2+
2+
active Ca ATPase Ca storage Hypoxia/hypercapnia ( Po 2 / Pco 2 )
2+
in sarcoplasmic reticulum Non-dihydropyridine Ca channel blockers
2+
Activated protein kinase A Ca
2+
channel phosphorylation Ca entry
2+
2+
Ca -induced Ca release
intracellular Ca 2+
+
+
2+
extracellular Na ( activity of Na /Ca
exchanger)
+
+
Digitalis (blocks Na /K pump
2+
+
+
intracellular Na Na /Ca
2+
exchanger activity intracellular Ca )
Preload Preload approximated by ventricular EDV; Vasodilators (eg, nitroglycerin) preload.
depends on venous tone and circulating blood
volume.
Afterload Afterload approximated by MAP. Arterial vasodilators (eg, hydralazine)
wall tension per Laplace’s law pressure Afterload.
afterload. ACE inhibitors and ARBs both preload and
afterload.
LV compensates for afterload by thickening Chronic hypertension ( MAP) LV
(hypertrophy) in order to wall stress. hypertrophy.
Myocardial oxygen Myocardial O 2 demand is by: Wall tension follows Laplace’s law:
demand Contractility Wall tension = pressure × radius
Afterload (proportional to arterial pressure)
heart Rate Wall stress = pressure × radius
Diameter of ventricle ( wall tension) 2 × wall thickness
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 284 11/7/19 4:24 PM