Page 358 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 358
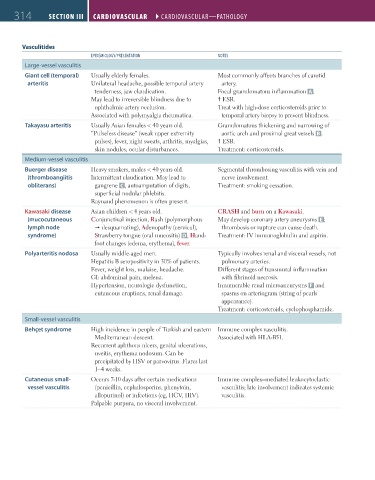
314 SECTION III CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY
Vasculitides
EPIdEMIOlOGY/PRESENTATION NOTES
Large-vessel vasculitis
Giant cell (temporal) Usually elderly females. Most commonly affects branches of carotid
arteritis Unilateral headache, possible temporal artery artery.
tenderness, jaw claudication. Focal granulomatous inflammation A .
May lead to irreversible blindness due to ESR.
ophthalmic artery occlusion. Treat with high-dose corticosteroids prior to
Associated with polymyalgia rheumatica. temporal artery biopsy to prevent blindness.
Takayasu arteritis Usually Asian females < 40 years old. Granulomatous thickening and narrowing of
“Pulseless disease” (weak upper extremity aortic arch and proximal great vessels B .
pulses), fever, night sweats, arthritis, myalgias, ESR.
skin nodules, ocular disturbances. Treatment: corticosteroids.
Medium-vessel vasculitis
Buerger disease Heavy smokers, males < 40 years old. Segmental thrombosing vasculitis with vein and
(thromboangiitis Intermittent claudication. May lead to nerve involvement.
obliterans) gangrene C , autoamputation of digits, Treatment: smoking cessation.
superficial nodular phlebitis.
Raynaud phenomenon is often present.
Kawasaki disease Asian children < 4 years old. CRASH and burn on a Kawasaki.
(mucocutaneous Conjunctival injection, Rash (polymorphous May develop coronary artery aneurysms E ;
lymph node desquamating), Adenopathy (cervical), thrombosis or rupture can cause death.
syndrome) Strawberry tongue (oral mucositis) D, Hand- Treatment: IV immunoglobulin and aspirin.
foot changes (edema, erythema), fever.
Polyarteritis nodosa Usually middle-aged men. Typically involves renal and visceral vessels, not
Hepatitis B seropositivity in 30% of patients. pulmonary arteries.
Fever, weight loss, malaise, headache. Different stages of transmural inflammation
GI: abdominal pain, melena. with fibrinoid necrosis.
Hypertension, neurologic dysfunction, Innumerable renal microaneurysms F and
cutaneous eruptions, renal damage. spasms on arteriogram (string of pearls
appearance).
Treatment: corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide.
Small-vessel vasculitis
Behçet syndrome High incidence in people of Turkish and eastern Immune complex vasculitis.
Mediterranean descent. Associated with HLA-B51.
Recurrent aphthous ulcers, genital ulcerations,
uveitis, erythema nodosum. Can be
precipitated by HSV or parvovirus. Flares last
1–4 weeks.
Cutaneous small- Occurs 7-10 days after certain medications Immune complex–mediated leukocytoclastic
vessel vasculitis (penicillin, cephalosporins, phenytoin, vasculitis; late involvement indicates systemic
allopurinol) or infections (eg, HCV, HIV). vasculitis.
Palpable purpura, no visceral involvement.
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 314 11/7/19 4:24 PM