Page 353 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 353
CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY SECTION III 309
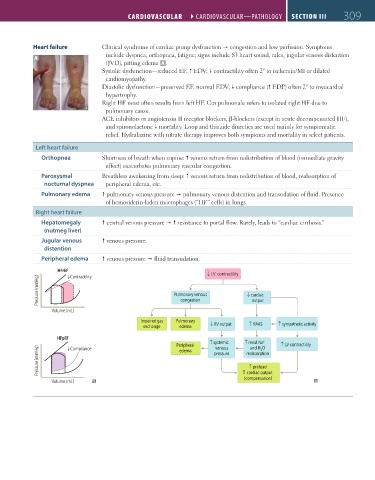
Heart failure Clinical syndrome of cardiac pump dysfunction congestion and low perfusion. Symptoms
A include dyspnea, orthopnea, fatigue; signs include S3 heart sound, rales, jugular venous distention
(JVD), pitting edema A .
Systolic dysfunction—reduced EF, EDV; contractility often 2° to ischemia/MI or dilated
cardiomyopathy.
Diastolic dysfunction—preserved EF, normal EDV; compliance ( EDP) often 2° to myocardial
hypertrophy.
Right HF most often results from left HF. Cor pulmonale refers to isolated right HF due to
pulmonary cause.
ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers, β-blockers (except in acute decompensated HF),
and spironolactone mortality. Loop and thiazide diuretics are used mainly for symptomatic
relief. Hydralazine with nitrate therapy improves both symptoms and mortality in select patients.
Left heart failure
Orthopnea Shortness of breath when supine: venous return from redistribution of blood (immediate gravity
effect) exacerbates pulmonary vascular congestion.
Paroxysmal Breathless awakening from sleep: venous return from redistribution of blood, reabsorption of
nocturnal dyspnea peripheral edema, etc.
Pulmonary edema pulmonary venous pressure pulmonary venous distention and transudation of fluid. Presence
of hemosiderin-laden macrophages (“HF” cells) in lungs.
Right heart failure
Hepatomegaly central venous pressure resistance to portal flow. Rarely, leads to “cardiac cirrhosis.”
(nutmeg liver)
Jugular venous venous pressure.
distention
Peripheral edema venous pressure fluid transudation.
HFrEF Contractility ↑ LV contractility
↓
Pressure (mmHg) Pulmonary venous ↑ cardiac
congestion
output
Volume (mL)
Impaired gas Pulmonary ↑ ↑
exchange edema ↑ RV output RAAS sympathetic activity
HFpEF +
Peripheral ↑ systemic ↑ renal Na ↑ LV contractility
venous
Pressure (mmHg) pressure reabsorption
and H O
↓
Compliance
edema
↑
preload
↑
cardiac output
(compensation)
Volume (mL)
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 309 11/7/19 4:24 PM