Page 354 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 354
310 SECTION III CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY
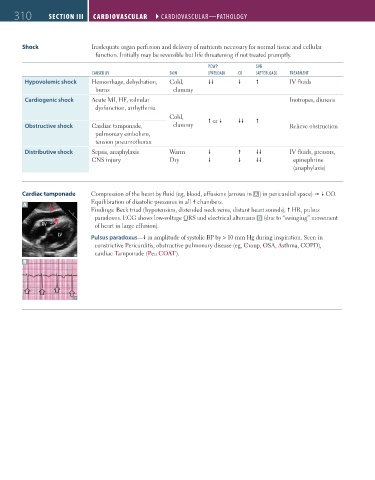
Shock Inadequate organ perfusion and delivery of nutrients necessary for normal tissue and cellular
function. Initially may be reversible but life threatening if not treated promptly.
PCWP SvR
CAuSEd bY SKIN (PRElOAd) CO (AFTERlOAd) TREATMENT
Hypovolemic shock Hemorrhage, dehydration, Cold, IV fluids
burns clammy
Cardiogenic shock Acute MI, HF, valvular Inotropes, diuresis
dysfunction, arrhythmia
Cold, or
Obstructive shock Cardiac tamponade, clammy Relieve obstruction
pulmonary embolism,
tension pneumothorax
Distributive shock Sepsis, anaphylaxis Warm IV fluids, pressors,
CNS injury Dry epinephrine
(anaphylaxis)
Cardiac tamponade Compression of the heart by fluid (eg, blood, effusions [arrows in A ] in pericardial space) CO.
Equilibration of diastolic pressures in all 4 chambers.
A
Findings: Beck triad (hypotension, distended neck veins, distant heart sounds), HR, pulsus
paradoxus. ECG shows low-voltage QRS and electrical alternans B (due to “swinging” movement
RV of heart in large effusion).
LV
Pulsus paradoxus— in amplitude of systolic BP by > 10 mm Hg during inspiration. Seen in
constrictive Pericarditis, obstructive pulmonary disease (eg, Croup, OSA, Asthma, COPD),
cardiac Tamponade (Pea COAT).
B
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 310 11/7/19 4:24 PM