Page 355 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 355
CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY SECTION III 311
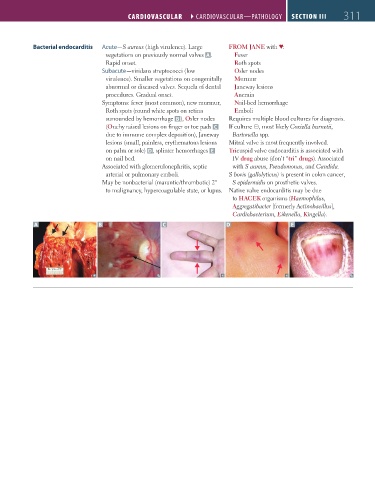
Bacterial endocarditis Acute—S aureus (high virulence). Large FROM JANE with ♥:
vegetations on previously normal valves A . Fever
Rapid onset. Roth spots
Subacute—viridans streptococci (low Osler nodes
virulence). Smaller vegetations on congenitally Murmur
abnormal or diseased valves. Sequela of dental Janeway lesions
procedures. Gradual onset. Anemia
Symptoms: fever (most common), new murmur, Nail-bed hemorrhage
Roth spots (round white spots on retina Emboli
surrounded by hemorrhage B ), Osler nodes Requires multiple blood cultures for diagnosis.
(Ouchy raised lesions on finger or toe pads C If culture ⊝, most likely Coxiella burnetii,
due to immune complex deposition), Janeway Bartonella spp.
lesions (small, painless, erythematous lesions Mitral valve is most frequently involved.
on palm or sole) D, splinter hemorrhages E Tricuspid valve endocarditis is associated with
on nail bed. IV drug abuse (don’t “tri” drugs). Associated
Associated with glomerulonephritis, septic with S aureus, Pseudomonas, and Candida.
arterial or pulmonary emboli. S bovis (gallolyticus) is present in colon cancer,
May be nonbacterial (marantic/thrombotic) 2° S epidermidis on prosthetic valves.
to malignancy, hypercoagulable state, or lupus. Native valve endocarditis may be due
to HACEK organisms (Haemophilus,
Aggregatibacter [formerly Actinobacillus],
Cardiobacterium, Eikenella, Kingella).
A B C D E
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 311 11/7/19 4:24 PM