Page 433 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 433
Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology seCtion iii 389
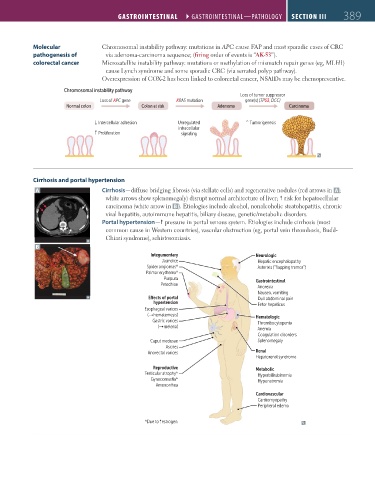
Molecular Chromosomal instability pathway: mutations in APC cause FAP and most sporadic cases of CRC
pathogenesis of via adenoma-carcinoma sequence; (firing order of events is “AK-53”).
colorectal cancer Microsatellite instability pathway: mutations or methylation of mismatch repair genes (eg, MLH1)
cause Lynch syndrome and some sporadic CRC (via serrated polyp pathway).
Overexpression of COX-2 has been linked to colorectal cancer, NSAIDs may be chemopreventive.
Chromosomal instability pathway
Loss of tumor suppressor
Loss of APC gene KRAS mutation gene(s) (TP53, DCC)
Normal colon Colon at risk Adenoma Carcinoma
Intercellular adhesion Unregulated Tumorigenesis
intracellular
Proliferation signaling
Cirrhosis and portal hypertension
A Cirrhosis—diffuse bridging fibrosis (via stellate cells) and regenerative nodules (red arrows in A ;
white arrows show splenomegaly) disrupt normal architecture of liver; risk for hepatocellular
carcinoma (white arrow in B ). Etiologies include alcohol, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, chronic
viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, biliary disease, genetic/metabolic disorders.
Portal hypertension— pressure in portal venous system. Etiologies include cirrhosis (most
common cause in Western countries), vascular obstruction (eg, portal vein thrombosis, Budd-
Chiari syndrome), schistosomiasis.
B
Integumentary Neurologic
Jaundice Hepatic encephalopathy
Spider angiomas* Asterixis (”flapping tremor”)
Palmar erythema*
Purpura Gastrointestinal
Petechiae
Anorexia
Nausea, vomiting
E ects of portal Dull abdominal pain
hypertension Fetor hepaticus
Esophageal varices
( hematemesis) Hematologic
Gastric varices Thrombocytopenia
( melena)
Anemia
Coagulation disorders
Caput medusae Splenomegaly
Ascites
Anorectal varices Renal
Hepatorenal syndrome
Reproductive Metabolic
Testicular atrophy* Hyperbilirubinemia
Gynecomastia* Hyponatremia
Amenorrhea
Cardiovascular
Cardiomyopathy
Peripheral edema
*Due to estrogen
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 389 11/7/19 4:42 PM