Page 467 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 467
Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—Pathology Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—Pathology SectIon III 423
Extrinsic hemolytic anemias
deScRIPtIon FIndIngS
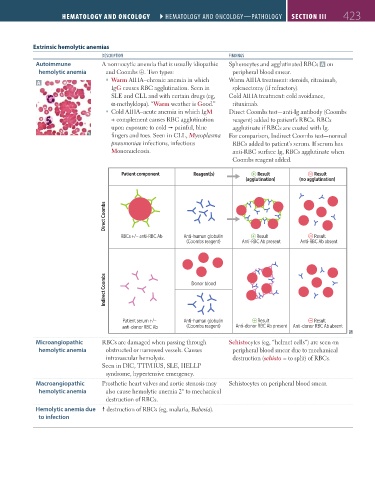
Autoimmune A normocytic anemia that is usually idiopathic Spherocytes and agglutinated RBCs A on
hemolytic anemia and Coombs ⊕. Two types: peripheral blood smear.
Warm AIHA–chronic anemia in which Warm AIHA treatment: steroids, rituximab,
A
IgG causes RBC agglutination. Seen in splenectomy (if refractory).
SLE and CLL and with certain drugs (eg, Cold AIHA treatment: cold avoidance,
α-methyldopa). “Warm weather is Good.” rituximab.
Cold AIHA–acute anemia in which IgM Direct Coombs test—anti-Ig antibody (Coombs
+ complement causes RBC agglutination reagent) added to patient’s RBCs. RBCs
upon exposure to cold painful, blue agglutinate if RBCs are coated with Ig.
fingers and toes. Seen in CLL, Mycoplasma For comparison, Indirect Coombs test—normal
pneumoniae infections, infectious RBCs added to patient’s serum. If serum has
Mononucleosis. anti-RBC surface Ig, RBCs agglutinate when
Coombs reagent added.
Patient component Reagent(s) Result Result
(agglutination) (no agglutination)
Direct Coombs
RBCs +/– anti-RBC Ab Anti-human globulin Result Result
(Coombs reagent) Anti-RBC Ab present Anti-RBC Ab absent
Indirect Coombs Donor blood
Patient serum +/– Anti-human globulin Result Result
anti-donor RBC Ab (Coombs reagent) Anti-donor RBC Ab present Anti-donor RBC Ab absent
Microangiopathic RBCs are damaged when passing through Schistocytes (eg, “helmet cells”) are seen on
hemolytic anemia obstructed or narrowed vessels. Causes peripheral blood smear due to mechanical
intravascular hemolysis. destruction (schisto = to split) of RBCs.
Seen in DIC, TTP/HUS, SLE, HELLP
syndrome, hypertensive emergency.
Macroangiopathic Prosthetic heart valves and aortic stenosis may Schistocytes on peripheral blood smear.
hemolytic anemia also cause hemolytic anemia 2° to mechanical
destruction of RBCs.
Hemolytic anemia due destruction of RBCs (eg, malaria, Babesia).
to infection
FAS1_2019_10-HemaOncol.indd 423 11/7/19 5:05 PM