Page 472 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 472
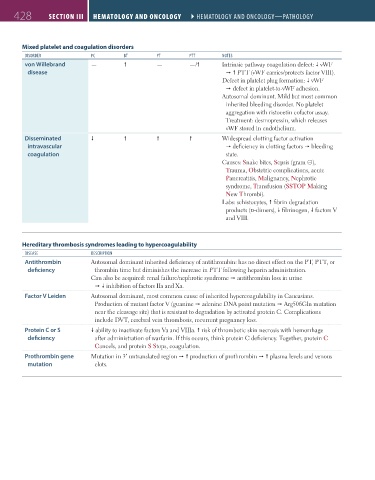
428 SectIon III Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—Pathology Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—Pathology
Mixed platelet and coagulation disorders
dISoRdeR Pc Bt Pt Ptt noteS
von Willebrand — — —/ Intrinsic pathway coagulation defect: vWF
disease PTT (vWF carries/protects factor VIII).
Defect in platelet plug formation: vWF
defect in platelet-to-vWF adhesion.
Autosomal dominant. Mild but most common
inherited bleeding disorder. No platelet
aggregation with ristocetin cofactor assay.
Treatment: desmopressin, which releases
vWF stored in endothelium.
Disseminated Widespread clotting factor activation
intravascular deficiency in clotting factors bleeding
coagulation state.
Causes: Snake bites, Sepsis (gram ⊝),
Trauma, Obstetric complications, acute
Pancreatitis, Malignancy, Nephrotic
syndrome, Transfusion (SSTOP Making
New Thrombi).
Labs: schistocytes, fibrin degradation
products (d-dimers), fibrinogen, factors V
and VIII.
Hereditary thrombosis syndromes leading to hypercoagulability
dISeaSe deScRIPtIon
Antithrombin Autosomal dominant inherited deficiency of antithrombin: has no direct effect on the PT, PTT, or
deficiency thrombin time but diminishes the increase in PTT following heparin administration.
Can also be acquired: renal failure/nephrotic syndrome antithrombin loss in urine
inhibition of factors IIa and Xa.
Factor V Leiden Autosomal dominant, most common cause of inherited hypercoagulability in Caucasians.
Production of mutant factor V (guanine adenine DNA point mutation Arg506Gln mutation
near the cleavage site) that is resistant to degradation by activated protein C. Complications
include DVT, cerebral vein thrombosis, recurrent pregnancy loss.
Protein C or S ability to inactivate factors Va and VIIIa. risk of thrombotic skin necrosis with hemorrhage
deficiency after administration of warfarin. If this occurs, think protein C deficiency. Together, protein C
Cancels, and protein S Stops, coagulation.
Prothrombin gene Mutation in 3′ untranslated region production of prothrombin plasma levels and venous
mutation clots.
FAS1_2019_10-HemaOncol.indd 428 11/7/19 5:05 PM