Page 463 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 463
Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—Pathology Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—Pathology SectIon III 419
Microcytic, hypochromic anemias (continued)
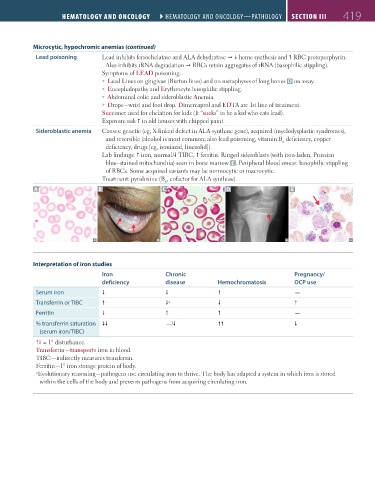
Lead poisoning Lead inhibits ferrochelatase and ALA dehydratase heme synthesis and RBC protoporphyrin.
Also inhibits rRNA degradation RBCs retain aggregates of rRNA (basophilic stippling).
Symptoms of LEAD poisoning:
Lead Lines on gingivae (Burton lines) and on metaphyses of long bones D on x-ray.
Encephalopathy and Erythrocyte basophilic stippling.
Abdominal colic and sideroblastic Anemia.
Drops—wrist and foot drop. Dimercaprol and EDTA are 1st line of treatment.
Succimer used for chelation for kids (It “sucks” to be a kid who eats lead).
Exposure risk in old houses with chipped paint.
Sideroblastic anemia Causes: genetic (eg, X-linked defect in ALA synthase gene), acquired (myelodysplastic syndromes),
and reversible (alcohol is most common; also lead poisoning, vitamin B deficiency, copper
6
deficiency, drugs [eg, isoniazid, linezolid]).
Lab findings: iron, normal/ TIBC, ferritin. Ringed sideroblasts (with iron-laden, Prussian
blue–stained mitochondria) seen in bone marrow E . Peripheral blood smear: basophilic stippling
of RBCs. Some acquired variants may be normocytic or macrocytic.
Treatment: pyridoxine (B , cofactor for ALA synthase).
6
A B C D E
Interpretation of iron studies
Iron Chronic Pregnancy/
deficiency disease Hemochromatosis OCP use
Serum iron —
Transferrin or TIBC a
Ferritin —
% transferrin saturation —/
(serum iron/TIBC)
= 1° disturbance.
Transferrin—transports iron in blood.
TIBC—indirectly measures transferrin.
Ferritin—1° iron storage protein of body.
a Evolutionary reasoning—pathogens use circulating iron to thrive. The body has adapted a system in which iron is stored
within the cells of the body and prevents pathogens from acquiring circulating iron.
FAS1_2019_10-HemaOncol.indd 419 11/7/19 5:05 PM