Page 468 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 468
424 SectIon III Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—Pathology Hematology and oncology ` hematology and oncology—Pathology
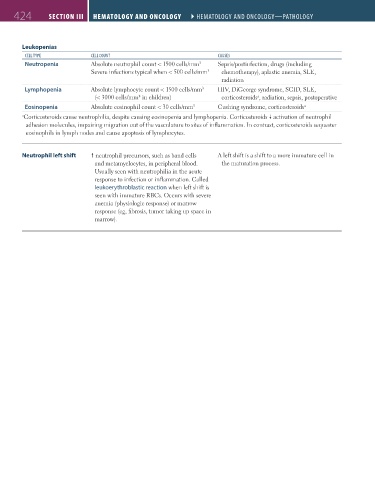
Leukopenias
cell tyPe cell coUnt caUSeS
Neutropenia Absolute neutrophil count < 1500 cells/mm 3 Sepsis/postinfection, drugs (including
Severe infections typical when < 500 cells/mm 3 chemotherapy), aplastic anemia, SLE,
radiation
Lymphopenia Absolute lymphocyte count < 1500 cells/mm HIV, DiGeorge syndrome, SCID, SLE,
3
(< 3000 cells/mm³ in children) corticosteroids , radiation, sepsis, postoperative
a
Eosinopenia Absolute eosinophil count < 30 cells/mm 3 Cushing syndrome, corticosteroids a
a Corticosteroids cause neutrophilia, despite causing eosinopenia and lymphopenia. Corticosteroids activation of neutrophil
adhesion molecules, impairing migration out of the vasculature to sites of inflammation. In contrast, corticosteroids sequester
eosinophils in lymph nodes and cause apoptosis of lymphocytes.
Neutrophil left shift neutrophil precursors, such as band cells A left shift is a shift to a more immature cell in
and metamyelocytes, in peripheral blood. the maturation process.
Usually seen with neutrophilia in the acute
response to infection or inflammation. Called
leukoerythroblastic reaction when left shift is
seen with immature RBCs. Occurs with severe
anemia (physiologic response) or marrow
response (eg, fibrosis, tumor taking up space in
marrow).
FAS1_2019_10-HemaOncol.indd 424 11/7/19 5:05 PM