Page 495 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 495
Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` anatomy and physiology Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` anatomy and physiology section iii 451
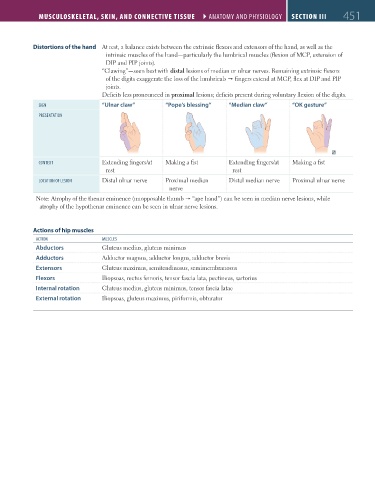
Distortions of the hand At rest, a balance exists between the extrinsic flexors and extensors of the hand, as well as the
intrinsic muscles of the hand—particularly the lumbrical muscles (flexion of MCP, extension of
DIP and PIP joints).
“Clawing”—seen best with distal lesions of median or ulnar nerves. Remaining extrinsic flexors
of the digits exaggerate the loss of the lumbricals fingers extend at MCP, flex at DIP and PIP
joints.
Deficits less pronounced in proximal lesions; deficits present during voluntary flexion of the digits.
sign “Ulnar claw” “Pope’s blessing” “Median claw” “OK gesture”
pREsEntation
ContEXt Extending fingers/at Making a fist Extending fingers/at Making a fist
rest rest
loCation oF lEsion Distal ulnar nerve Proximal median Distal median nerve Proximal ulnar nerve
nerve
Note: Atrophy of the thenar eminence (unopposable thumb “ape hand”) can be seen in median nerve lesions, while
atrophy of the hypothenar eminence can be seen in ulnar nerve lesions.
Actions of hip muscles
aCtion mUsClEs
Abductors Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus
Adductors Adductor magnus, adductor longus, adductor brevis
Extensors Gluteus maximus, semitendinosus, semimembranosus
Flexors Iliopsoas, rectus femoris, tensor fascia lata, pectineus, sartorius
Internal rotation Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fascia latae
External rotation Iliopsoas, gluteus maximus, piriformis, obturator
FAS1_2019_11-Musculo.indd 451 11/7/19 5:23 PM