Page 497 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 497
Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` anatomy and physiology Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` anatomy and physiology section iii 453
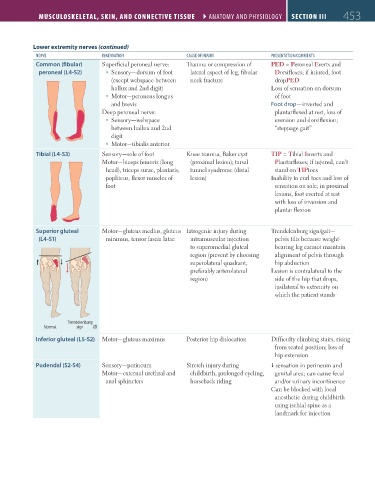
Lower extremity nerves (continued)
nERVE innERVation CaUsE oF inJURy pREsEntation/CommEnts
Common (fibular) Superficial peroneal nerve: Trauma or compression of PED = Peroneal Everts and
peroneal (L4-S2) Sensory—dorsum of foot lateral aspect of leg, fibular Dorsiflexes; if injured, foot
(except webspace between neck fracture dropPED
hallux and 2nd digit) Loss of sensation on dorsum
Motor—peroneus longus of foot
and brevis Foot drop—inverted and
Deep peroneal nerve: plantarflexed at rest, loss of
Sensory—webspace eversion and dorsiflexion;
between hallux and 2nd “steppage gait”
digit
Motor—tibialis anterior
Tibial (L4-S3) Sensory—sole of foot Knee trauma, Baker cyst TIP = Tibial Inverts and
Motor—biceps femoris (long (proximal lesion); tarsal Plantarflexes; if injured, can’t
head), triceps surae, plantaris, tunnel syndrome (distal stand on TIPtoes
popliteus, flexor muscles of lesion) Inability to curl toes and loss of
foot sensation on sole; in proximal
lesions, foot everted at rest
with loss of inversion and
plantar flexion
Superior gluteal Motor—gluteus medius, gluteus Iatrogenic injury during Trendelenburg sign/gait—
(L4-S1) minimus, tensor fascia latae intramuscular injection pelvis tilts because weight-
to superomedial gluteal bearing leg cannot maintain
region (prevent by choosing alignment of pelvis through
superolateral quadrant, hip abduction
preferably anterolateral Lesion is contralateral to the
region) side of the hip that drops,
ipsilateral to extremity on
which the patient stands
Trendelenburg
Normal sign
Inferior gluteal (L5-S2) Motor—gluteus maximus Posterior hip dislocation Difficulty climbing stairs, rising
from seated position; loss of
hip extension
Pudendal (S2-S4) Sensory—perineum Stretch injury during sensation in perineum and
Motor—external urethral and childbirth, prolonged cycling, genital area; can cause fecal
anal sphincters horseback riding and/or urinary incontinence
Can be blocked with local
anesthetic during childbirth
using ischial spine as a
landmark for injection
FAS1_2019_11-Musculo.indd 453 11/7/19 5:23 PM