Page 500 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 500
456 section iii Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` anatomy and physiology Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` anatomy and physiology
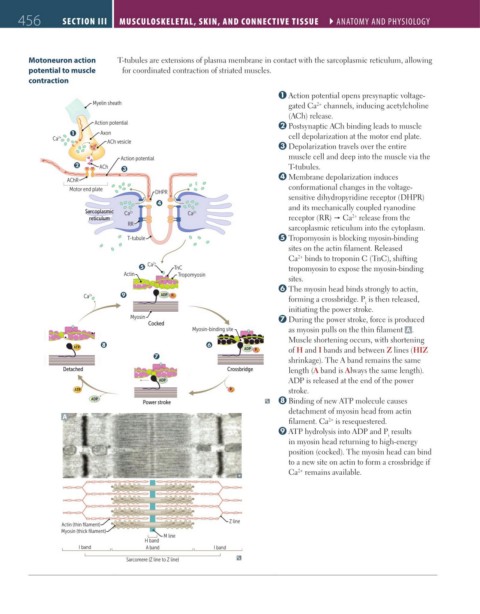
Motoneuron action T-tubules are extensions of plasma membrane in contact with the sarcoplasmic reticulum, allowing
potential to muscle for coordinated contraction of striated muscles.
contraction
Action potential opens presynaptic voltage-
Myelin sheath gated Ca channels, inducing acetylcholine
2+
(ACh) release.
Action potential Postsynaptic ACh binding leads to muscle
Q Axon
Ca 2+ cell depolarization at the motor end plate.
ACh vesicle
Depolarization travels over the entire
Action potential muscle cell and deep into the muscle via the
R ACh S T-tubules.
Membrane depolarization induces
AChR
Motor end plate conformational changes in the voltage-
DHPR
sensitive dihydropyridine receptor (DHPR)
T and its mechanically coupled ryanodine
Sarcoplasmic Ca 2+ Ca 2+
2+
reticulum receptor (RR) Ca release from the
RR
sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm.
T-tubule Tropomyosin is blocking myosin-binding
sites on the actin filament. Released
Ca binds to troponin C (TnC), shifting
2+
U Ca 2+ TnC tropomyosin to expose the myosin-binding
Actin Tropomyosin
sites.
The myosin head binds strongly to actin,
Ca Y ADP Pi forming a crossbridge. P is then released,
2+
i
initiating the power stroke.
Myosin During the power stroke, force is produced
Cocked
Myosin-binding site as myosin pulls on the thin filament A .
Muscle shortening occurs, with shortening
X V
ATP
ADP P i of H and I bands and between Z lines (HIZ
W
shrinkage). The A band remains the same
Detached Crossbridge length (A band is Always the same length).
ADP ADP is released at the end of the power
ATP P i stroke.
ADP Binding of new ATP molecule causes
Power stroke
detachment of myosin head from actin
A
filament. Ca is resequestered.
2+
ATP hydrolysis into ADP and P results
i
in myosin head returning to high-energy
position (cocked). The myosin head can bind
to a new site on actin to form a crossbridge if
Ca remains available.
2+
Z line
Actin (thin filament)
Myosin (thick filament)
M line
H band
I band A band I band
Sarcomere (Z line to Z line)
FAS1_2019_11-Musculo.indd 456 11/7/19 5:23 PM