Page 502 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 502
458 section iii Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` anatomy and physiology Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` pathology
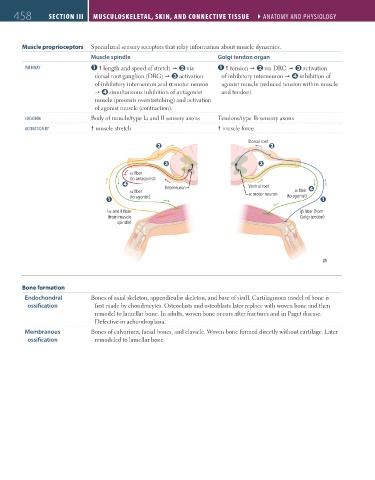
Muscle proprioceptors Specialized sensory receptors that relay information about muscle dynamics.
Muscle spindle Golgi tendon organ
pathWay length and speed of stretch via tension via DRG activation
dorsal root ganglion (DRG) activation of inhibitory interneuron inhibition of
of inhibitory interneuron and α motor neuron agonist muscle (reduced tension within muscle
simultaneous inhibition of antagonist and tendon)
muscle (prevents overstretching) and activation
of agonist muscle (contraction).
loCation Body of muscle/type Ia and II sensory axons Tendons/type Ib sensory axons
aCtiVation By muscle stretch muscle force
Dorsal root Dorsal root
α fiber α fiber
(to antagonist) (to antagonist)
Interneuron Interneuron Ventral root Ventral root
α fiber α fiber α fiber α fiber
(to agonist)
(to agonist) (to agonist) α motor neuron α motor neuron (to agonist)
Iα and II fiber Iα and II fiber Iβ fiber (from Iβ fiber (from
(from muscle (from muscle Golgi tendon) Golgi tendon)
spindle) spindle)
Bone formation
Endochondral Bones of axial skeleton, appendicular skeleton, and base of skull. Cartilaginous model of bone is
ossification first made by chondrocytes. Osteoclasts and osteoblasts later replace with woven bone and then
remodel to lamellar bone. In adults, woven bone occurs after fractures and in Paget disease.
Defective in achondroplasia.
Membranous Bones of calvarium, facial bones, and clavicle. Woven bone formed directly without cartilage. Later
ossification remodeled to lamellar bone.
FAS1_2019_11-Musculo.indd 458 11/7/19 5:23 PM