Page 544 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 544
500 SecTioN iii Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—AnAtomy And Physiology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—AnAtomy And Physiology
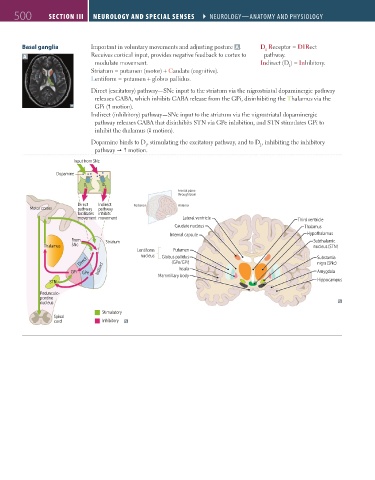
Basal ganglia Important in voluntary movements and adjusting posture A . D Receptor = D1Rect
1
A Receives cortical input, provides negative feedback to cortex to pathway.
modulate movement. Indirect (D ) = Inhibitory.
2
Striatum = putamen (motor) + Caudate (cognitive).
C
L Lentiform = putamen + globus pallidus.
T
Direct (excitatory) pathway—SNc input to the striatum via the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway
releases GABA, which inhibits GABA release from the GPi, disinhibiting the Thalamus via the
GPi ( motion).
Indirect (inhibitory) pathway—SNc input to the striatum via the nigrostriatal dopaminergic
pathway releases GABA that disinhibits STN via GPe inhibition, and STN stimulates GPi to
inhibit the thalamus ( motion).
Dopamine binds to D , stimulating the excitatory pathway, and to D , inhibiting the inhibitory
2
1
pathway motion.
Input from SNc
Dopamine
D 1 D 2
Frontal plane
through brain
Direct Indirect Posterior Anterior
Motor cortex pathway pathway
facilitates inhibits
movement movement Lateral ventricle Third ventricle
Caudate nucleus Thalamus
Internal capsule Hypothalamus
From Striatum Subthalamic
Thalamus SNc nucleus (STN)
Lentiform Putamen
nucleus Globus pallidus Substantia
Direct (GPe/GPi) nigra (SNc)
Insula
GPi GPe Indirect Mammillary body Amygdala
STN Hippocampus
Pedunculo-
pontine
nucleus
Stimulatory
Spinal
cord Inhibitory
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 500 11/8/19 7:39 AM