Page 545 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 545
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—AnAtomy And Physiology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—AnAtomy And Physiology SecTioN iii 501
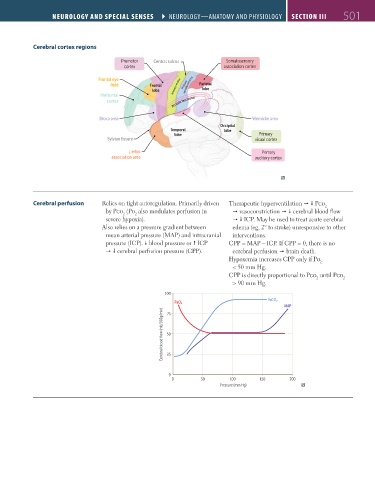
Cerebral cortex regions
Premotor Central sulcus Somatosensory
cortex association cortex
Frontal eye
field Frontal Primary somatosensory Parietal
lobe Primary motor lobe
Prefrontal
cortex Arcuate fasciculus
Broca area Wernicke area
Occipital
Temporal lobe
lobe Primary
Sylvian fissure visual cortex
Limbic Primary
association area auditory cortex
Cerebral perfusion Relies on tight autoregulation. Primarily driven Therapeutic hyperventilation Pco
2
by Pco (Po also modulates perfusion in vasoconstriction cerebral blood flow
2
2
severe hypoxia). ICP. May be used to treat acute cerebral
Also relies on a pressure gradient between edema (eg, 2° to stroke) unresponsive to other
mean arterial pressure (MAP) and intracranial interventions.
pressure (ICP). blood pressure or ICP CPP = MAP – ICP. If CPP = 0, there is no
cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP). cerebral perfusion brain death.
Hypoxemia increases CPP only if Po
2
< 50 mm Hg.
CPP is directly proportional to Pco until Pco
2
2
> 90 mm Hg.
100
PaCO₂
PaO₂
MAP
Cerebral blood flow (mL/100g/min) 50
75
25
0
0 50 100 150 200
Pressure (mm Hg)
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 501 11/8/19 7:39 AM