Page 558 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 558
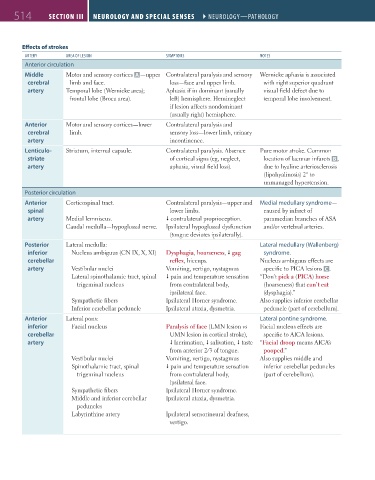
514 SecTioN iii Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology
Effects of strokes
Artery AreA oF lesion symPtoms notes
Anterior circulation
Middle Motor and sensory cortices A —upper Contralateral paralysis and sensory Wernicke aphasia is associated
cerebral limb and face. loss—face and upper limb. with right superior quadrant
artery Temporal lobe (Wernicke area); Aphasia if in dominant (usually visual field defect due to
frontal lobe (Broca area). left) hemisphere. Hemineglect temporal lobe involvement.
if lesion affects nondominant
(usually right) hemisphere.
Anterior Motor and sensory cortices—lower Contralateral paralysis and
cerebral limb. sensory loss—lower limb, urinary
artery incontinence.
Lenticulo- Striatum, internal capsule. Contralateral paralysis. Absence Pure motor stroke. Common
striate of cortical signs (eg, neglect, location of lacunar infarcts B ,
artery aphasia, visual field loss). due to hyaline arteriosclerosis
(lipohyalinosis) 2° to
unmanaged hypertension.
Posterior circulation
Anterior Corticospinal tract. Contralateral paralysis—upper and Medial medullary syndrome—
spinal lower limbs. caused by infarct of
artery Medial lemniscus. contralateral proprioception. paramedian branches of ASA
Caudal medulla—hypoglossal nerve. Ipsilateral hypoglossal dysfunction and/or vertebral arteries.
(tongue deviates ipsilaterally).
Posterior Lateral medulla: Lateral medullary (Wallenberg)
inferior Nucleus ambiguus (CN IX, X, XI) Dysphagia, hoarseness, gag syndrome.
cerebellar reflex, hiccups. Nucleus ambiguus effects are
artery Vestibular nuclei Vomiting, vertigo, nystagmus specific to PICA lesions C .
Lateral spinothalamic tract, spinal pain and temperature sensation “Don’t pick a (PICA) horse
trigeminal nucleus from contralateral body, (hoarseness) that can’t eat
ipsilateral face. (dysphagia).”
Sympathetic fibers Ipsilateral Horner syndrome. Also supplies inferior cerebellar
Inferior cerebellar peduncle Ipsilateral ataxia, dysmetria. peduncle (part of cerebellum).
Anterior Lateral pons: Lateral pontine syndrome.
inferior Facial nucleus Paralysis of face (LMN lesion vs Facial nucleus effects are
cerebellar UMN lesion in cortical stroke), specific to AICA lesions.
artery lacrimation, salivation, taste “Facial droop means AICA’s
from anterior 2⁄3 of tongue. pooped.”
Vestibular nuclei Vomiting, vertigo, nystagmus Also supplies middle and
Spinothalamic tract, spinal pain and temperature sensation inferior cerebellar peduncles
trigeminal nucleus from contralateral body, (part of cerebellum).
ipsilateral face.
Sympathetic fibers Ipsilateral Horner syndrome.
Middle and inferior cerebellar Ipsilateral ataxia, dysmetria.
peduncles
Labyrinthine artery Ipsilateral sensorineural deafness,
vertigo.
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 514 11/8/19 7:39 AM