Page 559 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 559
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology SecTioN iii 515
Effects of strokes (continued)
Artery AreA oF lesion symPtoms notes
Basilar artery Pons, medulla, lower midbrain. If RAS spared, consciousness is Locked-in syndrome (locked
preserved. in the basement).
Corticospinal and corticobulbar Quadriplegia; loss of voluntary
tracts. facial, mouth, and tongue
movements.
Ocular cranial nerve nuclei, Loss of horizontal, but not vertical,
paramedian pontine reticular eye movements.
formation.
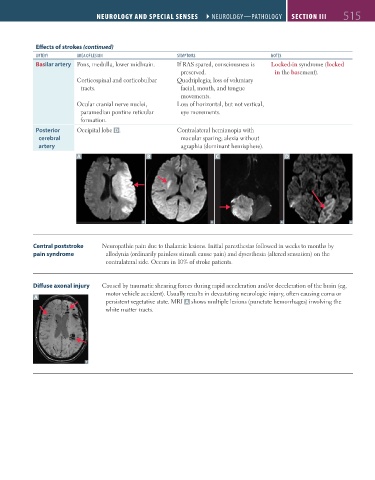
Posterior Occipital lobe D. Contralateral hemianopia with
cerebral macular sparing; alexia without
artery agraphia (dominant hemisphere).
A B C D
Central poststroke Neuropathic pain due to thalamic lesions. Initial paresthesias followed in weeks to months by
pain syndrome allodynia (ordinarily painless stimuli cause pain) and dysesthesia (altered sensation) on the
contralateral side. Occurs in 10% of stroke patients.
Diffuse axonal injury Caused by traumatic shearing forces during rapid acceleration and/or deceleration of the brain (eg,
motor vehicle accident). Usually results in devastating neurologic injury, often causing coma or
A
persistent vegetative state. MRI A shows multiple lesions (punctate hemorrhages) involving the
white matter tracts.
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 515 11/8/19 7:39 AM