Page 555 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 555
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—AnAtomy And Physiology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology SecTioN iii 511
` neurology—PAthology
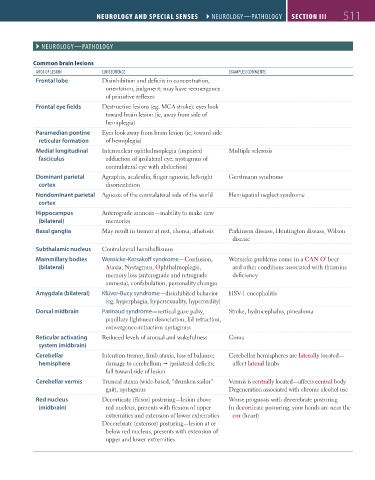
Common brain lesions
AreA oF lesion ConseQuenCe eXAmPles/Comments
Frontal lobe Disinhibition and deficits in concentration,
orientation, judgment; may have reemergence
of primitive reflexes
Frontal eye fields Destructive lesions (eg, MCA stroke): eyes look
toward brain lesion (ie, away from side of
hemiplegia)
Paramedian pontine Eyes look away from brain lesion (ie, toward side
reticular formation of hemiplegia)
Medial longitudinal Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (impaired Multiple sclerosis
fasciculus adduction of ipsilateral eye; nystagmus of
contralateral eye with abduction)
Dominant parietal Agraphia, acalculia, finger agnosia, left-right Gerstmann syndrome
cortex disorientation
Nondominant parietal Agnosia of the contralateral side of the world Hemispatial neglect syndrome
cortex
Hippocampus Anterograde amnesia—inability to make new
(bilateral) memories
Basal ganglia May result in tremor at rest, chorea, athetosis Parkinson disease, Huntington disease, Wilson
disease
Subthalamic nucleus Contralateral hemiballismus
Mammillary bodies Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome—Confusion, Wernicke problems come in a CAN O’ beer
(bilateral) Ataxia, Nystagmus, Ophthalmoplegia, and other conditions associated with thiamine
memory loss (anterograde and retrograde deficiency
amnesia), confabulation, personality changes
Amygdala (bilateral) Klüver-Bucy syndrome—disinhibited behavior HSV-1 encephalitis
(eg, hyperphagia, hypersexuality, hyperorality)
Dorsal midbrain Parinaud syndrome—vertical gaze palsy, Stroke, hydrocephalus, pinealoma
pupillary light-near dissociation, lid retraction,
convergence-retraction nystagmus
Reticular activating Reduced levels of arousal and wakefulness Coma
system (midbrain)
Cerebellar Intention tremor, limb ataxia, loss of balance; Cerebellar hemispheres are laterally located—
hemisphere damage to cerebellum ipsilateral deficits; affect lateral limbs
fall toward side of lesion
Cerebellar vermis Truncal ataxia (wide-based, “drunken sailor” Vermis is centrally located—affects central body
gait), nystagmus Degeneration associated with chronic alcohol use
Red nucleus Decorticate (flexor) posturing—lesion above Worse prognosis with decerebrate posturing
(midbrain) red nucleus, presents with flexion of upper In decorticate posturing, your hands are near the
extremities and extension of lower extremities cor (heart)
Decerebrate (extensor) posturing—lesion at or
below red nucleus, presents with extension of
upper and lower extremities
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 511 11/8/19 7:39 AM