Page 565 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 565
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology SecTioN iii 521
Neurodegenerative disorders (continued)
diseAse desCriPtion histologiC/gross Findings
Lewy body dementia Visual hallucinations (“haLewycinations”), Intracellular Lewy bodies A primarily in cortex.
dementia with fluctuating cognition/
alertness, REM sleep behavior disorder, and
parkinsonism. Called Lewy body dementia if
cognitive and motor symptom onset < 1 year
apart, otherwise considered dementia 2° to
Parkinson disease.
Vascular dementia Result of multiple arterial infarcts and/or MRI or CT shows multiple cortical and/or
chronic ischemia. subcortical infarcts.
Step-wise decline in cognitive ability with late-
onset memory impairment. 2nd most common
cause of dementia in elderly.
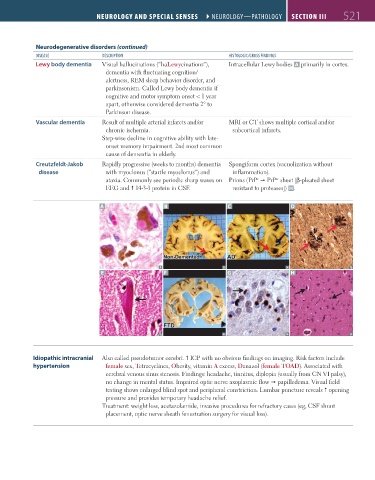
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Rapidly progressive (weeks to months) dementia Spongiform cortex (vacuolization without
disease with myoclonus (“startle myoclonus”) and inflammation).
ataxia. Commonly see periodic sharp waves on Prions (PrP PrP sheet [β-pleated sheet
c
sc
EEG and 14-3-3 protein in CSF. resistant to proteases]) H.
A B C D
E F G H
Idiopathic intracranial Also called pseudotumor cerebri. ICP with no obvious findings on imaging. Risk factors include
hypertension female sex, Tetracyclines, Obesity, vitamin A excess, Danazol (female TOAD). Associated with
cerebral venous sinus stenosis. Findings: headache, tinnitus, diplopia (usually from CN VI palsy),
no change in mental status. Impaired optic nerve axoplasmic flow papilledema. Visual field
testing shows enlarged blind spot and peripheral constriction. Lumbar puncture reveals opening
pressure and provides temporary headache relief.
Treatment: weight loss, acetazolamide, invasive procedures for refractory cases (eg, CSF shunt
placement, optic nerve sheath fenestration surgery for visual loss).
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 521 11/8/19 7:39 AM