Page 632 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 632
588 SeCTIOn III Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy
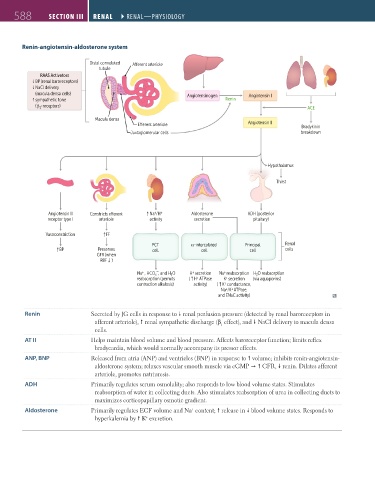
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Distal convoluted A erent arteriole
tubule
RAAS Activators
BP (renal baroreceptors)
↑
NaCl delivery
↑
(macula densa cells) Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I
sympathetic tone Renin
↑
-receptors)
(β 1 ACE
Macula densa
E erent arteriole Angiotensin II
Bradykinin
Juxtaglomerular cells breakdown
Hypothalamus
Thirst
+
↑
Angiotensin II Constricts e erent Na /H + Aldosterone ADH (posterior
receptor type I arteriole activity secretion pituitary)
Vasoconstriction ↑FF
PCT α-intercalated Principal Renal
↑BP Preserves cell cell cell cells
GFR (when
RBF ) ↑
+
Na + , HCO₃ , and H₂O H secretion Na reabsorption H₂O reabsorption
+
reabsorption (permits ( H ATPase K secretion (via aquaporins)
↑
+
+
+
contraction alkalosis) activity) ↑ ( K conductance,
Na /K ATPase,
+
+
and ENaC activity)
Renin Secreted by JG cells in response to renal perfusion pressure (detected by renal baroreceptors in
afferent arteriole), renal sympathetic discharge (β effect), and NaCl delivery to macula densa
1
cells.
AT II Helps maintain blood volume and blood pressure. Affects baroreceptor function; limits reflex
bradycardia, which would normally accompany its pressor effects.
ANP, BNP Released from atria (ANP) and ventricles (BNP) in response to volume; inhibits renin-angiotensin-
aldosterone system; relaxes vascular smooth muscle via cGMP GFR, renin. Dilates afferent
arteriole, promotes natriuresis.
ADH Primarily regulates serum osmolality; also responds to low blood volume states. Stimulates
reabsorption of water in collecting ducts. Also stimulates reabsorption of urea in collecting ducts to
maximizes corticopapillary osmotic gradient.
Aldosterone Primarily regulates ECF volume and Na content; release in blood volume states. Responds to
+
hyperkalemia by K excretion.
+
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 588 11/7/19 5:42 PM