Page 637 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 637
Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy SeCTIOn III 593
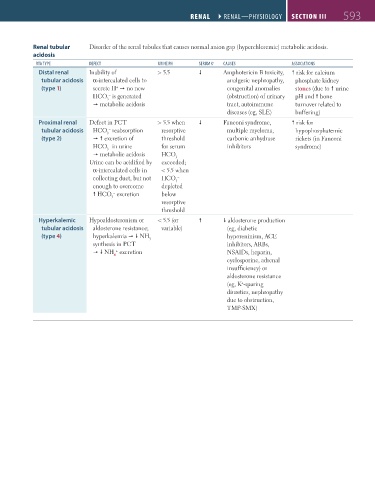
Renal tubular Disorder of the renal tubules that causes normal anion gap (hyperchloremic) metabolic acidosis.
acidosis
RtA tyPE DEFECt URiNE Ph sERUm K + CAUsEs AssoCiAtioNs
Distal renal Inability of > 5.5 Amphotericin B toxicity, risk for calcium
tubular acidosis α-intercalated cells to analgesic nephropathy, phosphate kidney
(type 1) secrete H no new congenital anomalies stones (due to urine
+
HCO is generated (obstruction) of urinary pH and bone
–
3
metabolic acidosis tract, autoimmune turnover related to
diseases (eg, SLE) buffering)
Proximal renal Defect in PCT > 5.5 when Fanconi syndrome, risk for
tubular acidosis HCO reabsorption resorptive multiple myeloma, hypophosphatemic
–
3
(type 2) excretion of threshold carbonic anhydrase rickets (in Fanconi
HCO in urine for serum inhibitors syndrome)
–
3
metabolic acidosis HCO
–
3
Urine can be acidified by exceeded;
α-intercalated cells in < 5.5 when
collecting duct, but not HCO
–
3
enough to overcome depleted
HCO excretion below
–
3
resorptive
threshold
Hyperkalemic Hypoaldosteronism or < 5.5 (or aldosterone production
tubular acidosis aldosterone resistance; variable) (eg, diabetic
(type 4) hyperkalemia NH hyporeninism, ACE
3
synthesis in PCT inhibitors, ARBs,
+
NH excretion NSAIDs, heparin,
4
cyclosporine, adrenal
insufficiency) or
aldosterone resistance
(eg, K -sparing
+
diuretics, nephropathy
due to obstruction,
TMP-SMX)
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 593 11/7/19 5:42 PM