Page 634 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 634
590 SeCTIOn III Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy
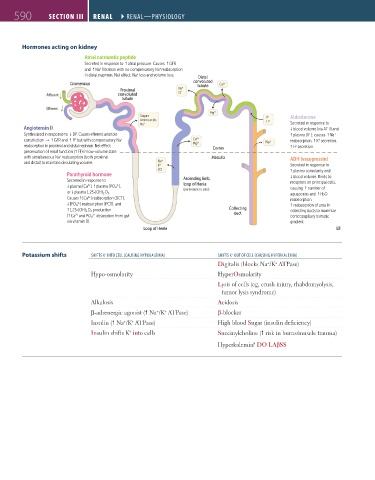
Hormones acting on kidney
Atrial natriuretic peptide
Secreted in response to ↑ atrial pressure. Causes ↑ GFR
+
and ↑ Na filtration with no compensatory Na reabsorption
+
+ loss and volume loss. Distal
convoluted
Glomerulus tubule Ca 2+
Proximal Na +
convoluted CI –
tubule
Mg 2+
Sugars K + Aldosterone
Amino acids H +
Na + Secreted in response to
Angiotensin II ↓ blood volume (via AT II) and
Synthesized in response to ↓ BP. Causes e erent arteriole ↑ plasma [K ]; causes ↑ Na +
+
constriction ↑ GFR and ↑ FF but with compensatory Na + Ca 2+ Na + reabsorption, ↑ K secretion,
+
↓
Mg 2+
reabsorption in proximal and distal nephron. Net e ect: Cortex H ↑ H secretion.
+
preservation of renal function ( ↑ FF) in low-volume state
+
with simultaneous Na reabsorption (both proximal Medulla
ADH (vasopressin)
and distal) to maintain circulating volume. Na +
K + Secreted in response to
2CI – ↑ plasma osmolarity and
Parathyroid hormone ↓ blood volume. Binds to
Secreted in response to Ascending limb, receptors on principal cells,
↓ plasma [Ca ], ↑ plasma [PO 4 ], loop of Henle
3–
2+
(permeable to salts) causing ↑ number of
or ↓ plasma 1,25-(OH) 2 D 3. aquaporins and ↑ H 2O
2+
Causes ↑ [Ca ] reabsorption (DCT), reabsorption.
3–
↓ [PO 4 ] reabsorption (PCT), and ↑ reabsorption of urea in
↑ 1,25-(OH) 2 D 3 production Collecting collecting ducts to maximize
( ↑ Ca and PO 4 absorption from gut duct corticopapillary osmotic
2+
3–
via vitamin D). gradient.
Loop of Henle
Potassium shifts shiFts K iNto CELL (CAUsiNg hyPoKALEmiA) shiFts K oUt oF CELL (CAUsiNg hyPERKALEmiA)
+
+
Digitalis (blocks Na /K ATPase)
+
+
Hypo-osmolarity HyperOsmolarity
Lysis of cells (eg, crush injury, rhabdomyolysis,
tumor lysis syndrome)
Alkalosis Acidosis
β-adrenergic agonist ( Na /K ATPase) β-blocker
+
+
Insulin ( Na /K ATPase) High blood Sugar (insulin deficiency)
+
+
Insulin shifts K into cells Succinylcholine ( risk in burns/muscle trauma)
+
Hyperkalemia? DO LAβSS
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 590 11/7/19 5:42 PM