Page 635 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 635
Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy Renal ` RENAL—PhysioLogy SeCTIOn III 591
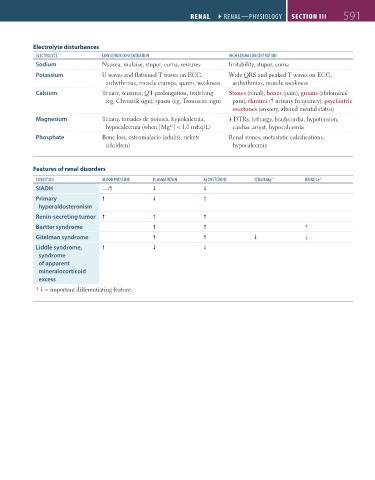
Electrolyte disturbances
ELECtRoLytE LoW sERUm CoNCENtRAtioN high sERUm CoNCENtRAtioN
Sodium Nausea, malaise, stupor, coma, seizures Irritability, stupor, coma
Potassium U waves and flattened T waves on ECG, Wide QRS and peaked T waves on ECG,
arrhythmias, muscle cramps, spasm, weakness arrhythmias, muscle weakness
Calcium Tetany, seizures, QT prolongation, twitching Stones (renal), bones (pain), groans (abdominal
(eg, Chvostek sign), spasm (eg, Trousseau sign) pain), thrones ( urinary frequency), psychiatric
overtones (anxiety, altered mental status)
Magnesium Tetany, torsades de pointes, hypokalemia, DTRs, lethargy, bradycardia, hypotension,
hypocalcemia (when [Mg ] < 1.0 mEq/L) cardiac arrest, hypocalcemia
2+
Phosphate Bone loss, osteomalacia (adults), rickets Renal stones, metastatic calcifications,
(children) hypocalcemia
Features of renal disorders
CoNDitioN bLooD PREssURE PLAsmA RENiN ALDostERoNE sERUm mg 2+ URiNE Ca 2+
SIADH —/
Primary
hyperaldosteronism
Renin-secreting tumor
Bartter syndrome
Gitelman syndrome
Liddle syndrome,
syndrome
of apparent
mineralocorticoid
excess
= important differentiating feature.
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 591 11/7/19 5:42 PM