Page 683 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 683
RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PATHOlOgy RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PATHOlOgy SectioN iii 639
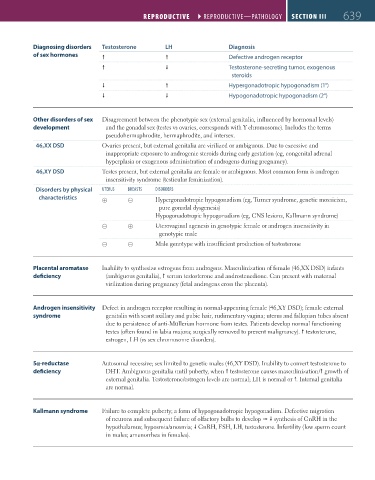
Diagnosing disorders Testosterone LH Diagnosis
of sex hormones Defective androgen receptor
Testosterone-secreting tumor, exogenous
steroids
Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism (1°)
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (2°)
Other disorders of sex Disagreement between the phenotypic sex (external genitalia, influenced by hormonal levels)
development and the gonadal sex (testes vs ovaries, corresponds with Y chromosome). Includes the terms
pseudohermaphrodite, hermaphrodite, and intersex.
46,XX DSD Ovaries present, but external genitalia are virilized or ambiguous. Due to excessive and
inappropriate exposure to androgenic steroids during early gestation (eg, congenital adrenal
hyperplasia or exogenous administration of androgens during pregnancy).
46,XY DSD Testes present, but external genitalia are female or ambiguous. Most common form is androgen
insensitivity syndrome (testicular feminization).
Disorders by physical UTERUS bREASTS DISORDERS
characteristics ⊕ ⊝ Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism (eg, Turner syndrome, genetic mosaicism,
pure gonadal dysgenesis)
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (eg, CNS lesions, Kallmann syndrome)
⊝ ⊕ Uterovaginal agenesis in genotypic female or androgen insensitivity in
genotypic male
⊝ ⊝ Male genotype with insufficient production of testosterone
Placental aromatase Inability to synthesize estrogens from androgens. Masculinization of female (46,XX DSD) infants
deficiency (ambiguous genitalia), serum testosterone and androstenedione. Can present with maternal
virilization during pregnancy (fetal androgens cross the placenta).
Androgen insensitivity Defect in androgen receptor resulting in normal-appearing female (46,XY DSD); female external
syndrome genitalia with scant axillary and pubic hair, rudimentary vagina; uterus and fallopian tubes absent
due to persistence of anti-Müllerian hormone from testes. Patients develop normal functioning
testes (often found in labia majora; surgically removed to prevent malignancy). testosterone,
estrogen, LH (vs sex chromosome disorders).
5α-reductase Autosomal recessive; sex limited to genetic males (46,XY DSD). Inability to convert testosterone to
deficiency DHT. Ambiguous genitalia until puberty, when testosterone causes masculinization/ growth of
external genitalia. Testosterone/estrogen levels are normal; LH is normal or . Internal genitalia
are normal.
Kallmann syndrome Failure to complete puberty; a form of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Defective migration
of neurons and subsequent failure of olfactory bulbs to develop synthesis of GnRH in the
hypothalamus; hyposmia/anosmia; GnRH, FSH, LH, testosterone. Infertility (low sperm count
in males; amenorrhea in females).
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 639 11/7/19 5:52 PM