Page 688 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 688
644 SectioN iii RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PATHOlOgy RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PATHOlOgy
Vulvar pathology
Non-neoplastic
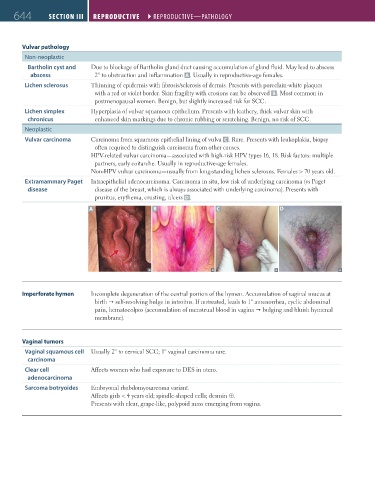
Bartholin cyst and Due to blockage of Bartholin gland duct causing accumulation of gland fluid. May lead to abscess
abscess 2° to obstruction and inflammation A . Usually in reproductive-age females.
Lichen sclerosus Thinning of epidermis with fibrosis/sclerosis of dermis. Presents with porcelain-white plaques
with a red or violet border. Skin fragility with erosions can be observed B . Most common in
postmenopausal women. Benign, but slightly increased risk for SCC.
Lichen simplex Hyperplasia of vulvar squamous epithelium. Presents with leathery, thick vulvar skin with
chronicus enhanced skin markings due to chronic rubbing or scratching. Benign, no risk of SCC.
Neoplastic
Vulvar carcinoma Carcinoma from squamous epithelial lining of vulva C . Rare. Presents with leukoplakia, biopsy
often required to distinguish carcinoma from other causes.
HPV-related vulvar carcinoma—associated with high-risk HPV types 16, 18. Risk factors: multiple
partners, early coitarche. Usually in reproductive-age females.
Non-HPV vulvar carcinoma—usually from long-standing lichen sclerosus. Females > 70 years old.
Extramammary Paget Intraepithelial adenocarcinoma. Carcinoma in situ, low risk of underlying carcinoma (vs Paget
disease disease of the breast, which is always associated with underlying carcinoma). Presents with
pruritus, erythema, crusting, ulcers D.
A B C D
Imperforate hymen Incomplete degeneration of the central portion of the hymen. Accumulation of vaginal mucus at
birth self-resolving bulge in introitus. If untreated, leads to 1° amenorrhea, cyclic abdominal
pain, hematocolpos (accumulation of menstrual blood in vagina bulging and bluish hymenal
membrane).
Vaginal tumors
Vaginal squamous cell Usually 2° to cervical SCC; 1° vaginal carcinoma rare.
carcinoma
Clear cell Affects women who had exposure to DES in utero.
adenocarcinoma
Sarcoma botryoides Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma variant.
Affects girls < 4 years old; spindle-shaped cells; desmin ⊕.
Presents with clear, grape-like, polypoid mass emerging from vagina.
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 644 11/7/19 5:52 PM