Page 685 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 685
RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PATHOlOgy RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PATHOlOgy SectioN iii 641
Pregnancy complications (continued)
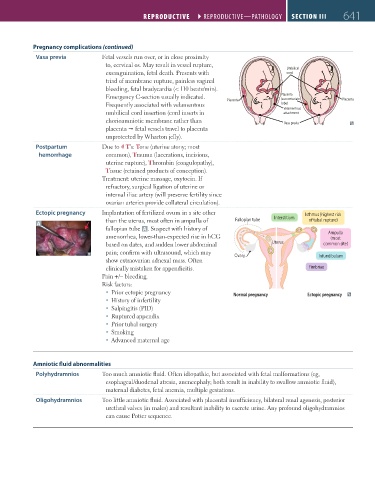
Vasa previa Fetal vessels run over, or in close proximity
to, cervical os. May result in vessel rupture, Umbilical
exsanguination, fetal death. Presents with cord
triad of membrane rupture, painless vaginal
bleeding, fetal bradycardia (< 110 beats/min).
Emergency C-section usually indicated. Placenta Placenta Placenta
(succenturiate
Frequently associated with velamentous lobe)
umbilical cord insertion (cord inserts in Velamentous
attachment
chorioamniotic membrane rather than Vasa previa
placenta fetal vessels travel to placenta
unprotected by Wharton jelly).
Postpartum Due to 4 T’s: Tone (uterine atony; most
hemorrhage common), Trauma (lacerations, incisions,
uterine rupture), Thrombin (coagulopathy),
Tissue (retained products of conception).
Treatment: uterine massage, oxytocin. If
refractory, surgical ligation of uterine or
internal iliac artery (will preserve fertility since
ovarian arteries provide collateral circulation).
Ectopic pregnancy Implantation of fertilized ovum in a site other Isthmus (highest risk
than the uterus, most often in ampulla of Fallopian tube Interstitium of tubal rupture)
A
fallopian tube A . Suspect with history of
amenorrhea, lower-than-expected rise in hCG Ampulla
(most
based on dates, and sudden lower abdominal Uterus common site)
pain; confirm with ultrasound, which may Ovary
show extraovarian adnexal mass. Often Infundibulum
clinically mistaken for appendicitis. Fimbriae
Pain +/− bleeding.
Risk factors:
Prior ectopic pregnancy Normal pregnancy Ectopic pregnancy
History of infertility
Salpingitis (PID)
Ruptured appendix
Prior tubal surgery
Smoking
Advanced maternal age
Amniotic fluid abnormalities
Polyhydramnios Too much amniotic fluid. Often idiopathic, but associated with fetal malformations (eg,
esophageal/duodenal atresia, anencephaly; both result in inability to swallow amniotic fluid),
maternal diabetes, fetal anemia, multiple gestations.
Oligohydramnios Too little amniotic fluid. Associated with placental insufficiency, bilateral renal agenesis, posterior
urethral valves (in males) and resultant inability to excrete urine. Any profound oligohydramnios
can cause Potter sequence.
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 641 11/7/19 5:52 PM