Page 141 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 141
Chapter 2 Common processes and techniques
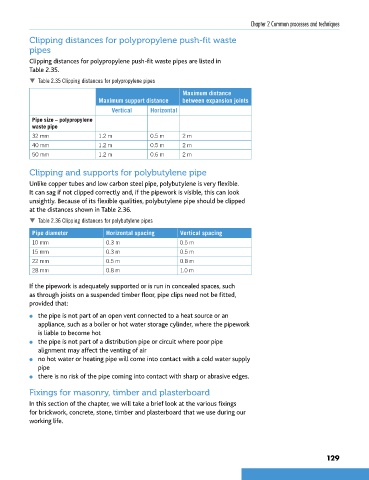
Clipping distances for polypropylene push-fit waste
pipes
Clipping distances for polypropylene push-fit waste pipes are listed in
Table 2.35.
Table 2.35 Clipping distances for polypropylene pipes
Maximum distance
Maximum support distance between expansion joints
Vertical Horizontal
Pipe size – polypropylene
waste pipe
32 mm 1.2 m 0.5 m 2 m
40 mm 1.2 m 0.5 m 2 m
50 mm 1.2 m 0.6 m 2 m
Clipping and supports for polybutylene pipe
Unlike copper tubes and low carbon steel pipe, polybutylene is very flexible.
It can sag if not clipped correctly and, if the pipework is visible, this can look
unsightly. Because of its flexible qualities, polybutylene pipe should be clipped
at the distances shown in Table 2.36.
Table 2.36 Clipping distances for polybutylene pipes
Pipe diameter Horizontal spacing Vertical spacing
10 mm 0.3 m 0.5 m
15 mm 0.3 m 0.5 m
22 mm 0.5 m 0.8 m
28 mm 0.8 m 1.0 m
If the pipework is adequately supported or is run in concealed spaces, such
as through joists on a suspended timber floor, pipe clips need not be fitted,
provided that:
● the pipe is not part of an open vent connected to a heat source or an
appliance, such as a boiler or hot water storage cylinder, where the pipework
is liable to become hot
● the pipe is not part of a distribution pipe or circuit where poor pipe
alignment may affect the venting of air
● no hot water or heating pipe will come into contact with a cold water supply
pipe
● there is no risk of the pipe coming into contact with sharp or abrasive edges.
Fixings for masonry, timber and plasterboard
In this section of the chapter, we will take a brief look at the various fixings
for brickwork, concrete, stone, timber and plasterboard that we use during our
working life.
129
9781510416482.indb 129 29/03/19 8:54 PM