Page 160 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 160
The City & Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1
SI base units
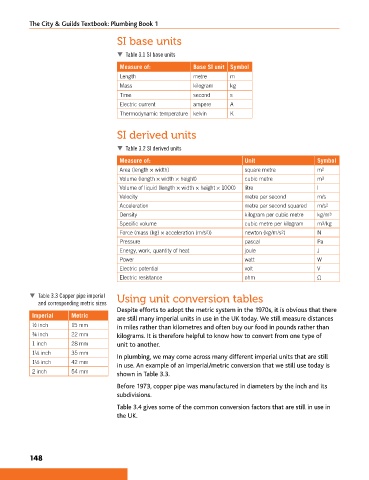
Table 3.1 SI base units
Measure of: Base SI unit Symbol
Length metre m
Mass kilogram kg
Time second s
Electric current ampere A
Thermodynamic temperature kelvin K
SI derived units
Table 3.2 SI derived units
Measure of: Unit Symbol
Area (length × width) square metre m 2
Volume (length × width × height) cubic metre m 3
Volume of liquid (length × width × height × 1000) litre l
Velocity metre per second m/s
Acceleration metre per second squared m/s 2
Density kilogram per cubic metre kg/m 3
Specific volume cubic metre per kilogram m 3 /kg
Force (mass (kg) × acceleration (m/s 2 )) newton (kg/m/s 2 ) N
Pressure pascal Pa
Energy, work, quantity of heat joule J
Power watt W
Electric potential volt V
Electric resistance ohm Ω
Table 3.3 Copper pipe imperial Using unit conversion tables
and corresponding metric sizes
Despite efforts to adopt the metric system in the 1970s, it is obvious that there
Imperial Metric
are still many imperial units in use in the UK today. We still measure distances
½ inch 15 mm in miles rather than kilometres and often buy our food in pounds rather than
¾ inch 22 mm kilograms. It is therefore helpful to know how to convert from one type of
1 inch 28 mm unit to another.
1¼ inch 35 mm
In plumbing, we may come across many different imperial units that are still
1½ inch 42 mm
in use. An example of an imperial/metric conversion that we still use today is
2 inch 54 mm shown in Table 3.3.
Before 1973, copper pipe was manufactured in diameters by the inch and its
subdivisions.
Table 3.4 gives some of the common conversion factors that are still in use in
the UK.
148
9781510416482.indb 148 29/03/19 8:54 PM