Page 164 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 164
The City & Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1
Plastics
Just as plumbers should know their metals, they should also know their plastics
if mistakes during installation are to be avoided. There are many different
plastics that plumbers use in their day-to-day work for installing hot and cold
water supplies, central heating, guttering and rainwater pipes, and above-and
below-ground drainage systems.
There are two basic types of plastics: thermoplastics and thermosetting.
1 Thermoplastics: a thermoplastic is a type of plastic made from polymer
resins that becomes liquid-form when heated and hard when cooled. When
frozen, however, a thermoplastic becomes brittle and subject to fracture.
These characteristics are reversible and it can be reheated, reshaped and
frozen repeatedly. This quality also makes thermoplastics recyclable.
There are many different types of thermoplastics, some of which are used
extensively in plumbing systems. Each type varies in crystalline organisation
and density. Table 3.8 lists the plastics commonly used in the plumbing
industry and describes what they are used for.
2 Thermosetting: thermosetting plastics, such as polyester and epoxies, are
rigid plastics, resistant to higher temperatures than thermoplastics. Once it
has set, a thermosetting plastic cannot be remoulded. Its shape is permanent
and it does not melt when heated.
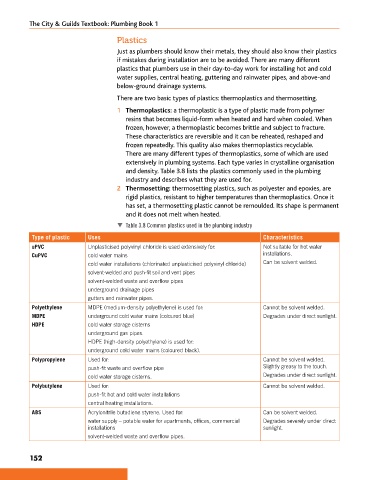
Table 3.8 Common plastics used in the plumbing industry
Type of plastic Uses Characteristics
uPVC Unplasticised polyvinyl chloride is used extensively for: Not suitable for hot water
CuPVC cold water mains installations.
cold water installations (chlorinated unplasticised polyvinyl chloride) Can be solvent welded.
solvent-welded and push-fit soil and vent pipes
solvent-welded waste and overflow pipes
underground drainage pipes
gutters and rainwater pipes.
Polyethylene MDPE (medium-density polyethylene) is used for: Cannot be solvent welded.
MDPE underground cold water mains (coloured blue) Degrades under direct sunlight.
HDPE cold water storage cisterns
underground gas pipes.
HDPE (high-density polyethylene) is used for:
underground cold water mains (coloured black).
Polypropylene Used for: Cannot be solvent welded.
push-fit waste and overflow pipe Slightly greasy to the touch.
cold water storage cisterns. Degrades under direct sunlight.
Polybutylene Used for: Cannot be solvent welded.
push-fit hot and cold water installations
central heating installations.
ABS Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene. Used for: Can be solvent welded.
water supply – potable water for apartments, offices, commercial Degrades severely under direct
installations sunlight.
solvent-welded waste and overflow pipes.
152
9781510416482.indb 152 29/03/19 8:54 PM