Page 203 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 203
Chapter 3 Scientific principles
Consider a basic series circuit with one 40 watt light bulb connected to a 230 V
electricity supply. The bulb glows at full brightness as it receives a full 230 V. If
Ohm’s law is applied, the resistance in the circuit is as follows:
P 40 watts
I = (from the power triangle) to find the current (I) = = 0.174 A
V 230 volts
V 230
R = = = 1322.6Ω
I 0.174
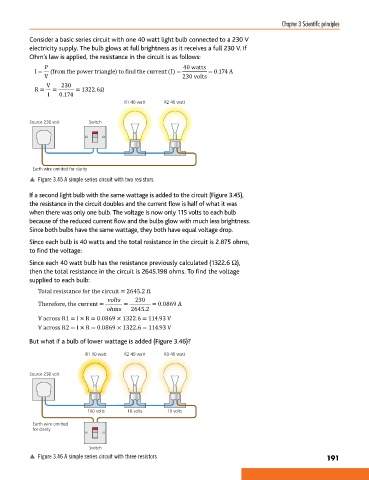
R1 40 watt R2 40 watt
Source 230 volt Switch
Earth wire omitted for clarity
p Figure 3.45 A simple series circuit with two resistors
If a second light bulb with the same wattage is added to the circuit (Figure 3.45),
the resistance in the circuit doubles and the current flow is half of what it was
when there was only one bulb. The voltage is now only 115 volts to each bulb
because of the reduced current flow and the bulbs glow with much less brightness.
Since both bulbs have the same wattage, they both have equal voltage drop.
Since each bulb is 40 watts and the total resistance in the circuit is 2.875 ohms,
to find the voltage:
Since each 40 watt bulb has the resistance previously calculated (1322.6 Ω),
then the total resistance in the circuit is 2645.198 ohms. To find the voltage
supplied to each bulb:
Total resistance for the circuit = 2645.2 Ω
volts 230
Therefore, the current = = = 0.0869 A
ohms 2645.2
V across R1 = I × R = 0.0869 × 1322.6 = 114.93 V
V across R2 = I × R = 0.0869 × 1322.6 = 114.93 V
But what if a bulb of lower wattage is added (Figure 3.46)?
R1 10 watt R2 40 watt R3 40 watt
Source 230 volt
100 volts 10 volts 10 volts
Earth wire omitted
for clarity
Switch
p Figure 3.46 A simple series circuit with three resistors 191
9781510416482.indb 191 29/03/19 8:55 PM