Page 204 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 204
The City & Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1
The third bulb added is a 230 V, 10 W bulb, so we first need to calculate its
resistance:
P
I = (from the power triangle) to find the current:
V
10 watts
(I) = = 0.0435 amps
230 volts
V 230
R = = = 5287 Ω
I 0.0435
ACTIVITY Total resistance in the circuit = 5287 + 1322.6 + 1322.6 = 7932.2 Ω
V 230
Therefore: = I = = 0.0290 amps
Series circuits R 7932.2
An electrical circuit in V at R1 = I × R = 0.0290 × 5287 = 153.32 V
series has four light bulbs V at R2 = I × R = 0.0290 × 1322.6 = 38.35 V
connected to it, one at 40
watts, one at 60 watts and V at R3 = I × R = 0.0290 × 1322.6 = 38.35 V
two at 100 watts. Determine Total volts = 230 V
the voltage consumed by This shows that the bulb with the highest resistance (10 W) would draw
each light bulb when the
voltage is 110. more of the voltage than the other two bulbs and would glow almost at full
brightness, whereas the other 40 W bulbs would hardly glow at all.
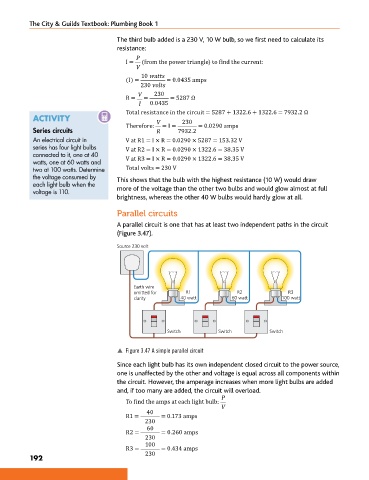
Parallel circuits
A parallel circuit is one that has at least two independent paths in the circuit
(Figure 3.47).
Source 230 volt
Earth wire
omitted for R1 R2 R3
clarity 40 watt 60 watt 100 watt
Switch Switch Switch
p Figure 3.47 A simple parallel circuit
Since each light bulb has its own independent closed circuit to the power source,
one is unaffected by the other and voltage is equal across all components within
the circuit. However, the amperage increases when more light bulbs are added
and, if too many are added, the circuit will overload.
P
To find the amps at each light bulb:
V
40
R1 = = 0.173 amps
230
60
R2 = = 0.260 amps
230
100
R3 = = 0.434 amps
192 230
9781510416482.indb 192 29/03/19 8:55 PM